Hot off the press
Robert A.
Hill
and
Andrew
Sutherland
Department of Chemistry, Glasgow University, Glasgow, UK G12 8QQ. E-mail: bobh@chem.gla.ac.uk; andrews@chem.gla.ac.uk
First published on 19th January 2005
Abstract
A personal selection of 39 recent papers is presented covering various aspects of current developments in bioorganic chemistry and novel natural products such as perforatumone that has been isolated from Hypericum perforatum used in Chinese herbal medicine.
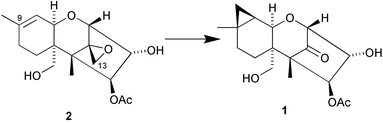
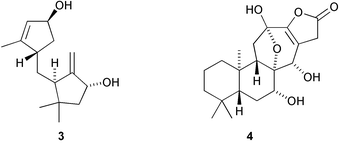
Tenuipesine A 1, a metabolite of Paecilomyces tenuipes, has a rearranged skeleton that is apparently formed from the co-occurring trichothecane 2 by C-13 migration to the C-9 double bond to form a cyclopropane (Y. Oshima and co-workers, Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 4531). Godotol A 3, isolated from Pluchea arabica, has a new sesquiterpenoid skeleton of unknown biosynthetic origin (M. O. Fatope et al., J. Nat. Prod., 2004, 67, 1925). The diterpenoid skeleton of bannaringaolide A 4, from Suregada multiflora, is possibly formed by ring expansion of a pimarane derivative (M. I. Choudhary and co-workers, J. Nat. Prod., 2004, 67, 1789).
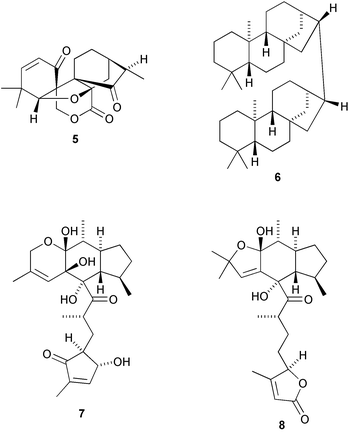
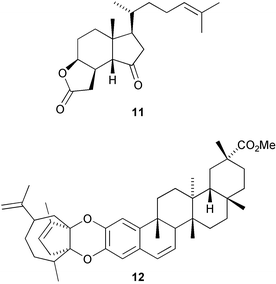
The genus Isodon (Rabdosia) produces diterpenoid constituents with highly oxygenated and rearranged skeletons. The structure of maoecrystal V 5, from Isodon eriocalyx, was confirmed by X-ray analysis as possessing a new rearranged norkaurane skeleton (H.-D. Sun and co-workers, Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 4327). Annoglabayin 6, from fruits of Annona glabra, is a dimeric norkaurane derivative with a carbon linkage between C-16 of each unit (C.-Y. Chen and co-workers, J. Nat. Prod., 2004, 67, 1942). Biosynthetic pathways have been proposed for two novel sesterterpenoids, leucosesterterpenone 7 and leucosesterlactone 8, isolated from Leucosceptrum canum (M. I. Choudhary et al., Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 4139).
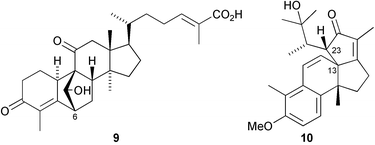
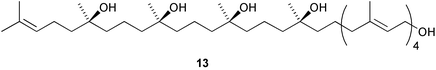
A new cucurbitacin, siraitic acid F 9, with a novel 6,19-linkage, has been isolated from the roots of Siraitia grosvenorii (D.-H. Chen and co-workers, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 2005, 7, 37). A novel 13,23-linkage is found in the rearranged norergostane derivative, agariblazeispirol 10, a metabolite of Agaricus blazei (M. Hirotani et al., Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 189). The degraded steroid aplykurodinone 1 11 has been isolated from the skin of the sea hare Syphonota geographica (M. Gavagnin et al., Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 617). Cheiloclines A–I, such as cheilocline A 12, have been isolated from the root bark of Cheiloclinium hippocratioides (A. G. Ravelo and co-workers, Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 429). The cheiloclines are adducts of nortriterpenoid and sesquiterpenoid moieties. The stereochemistry of glisoprenin A 13, an acyl CoA transferase inhibitor isolated from a Gliocladium species, has been established by NMR methods and by total synthesis (Y. Kishi and co-workers, Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 4719; 4726).
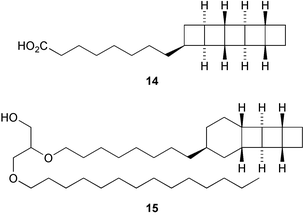
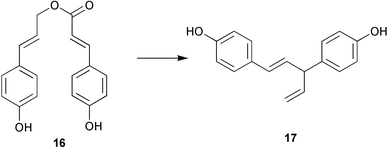
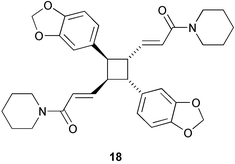
The membrane lipids of anaerobic ammonium oxidising (anammox) bacteria contain interesting ladderane fatty acids such as pentacycloanammoxic acid 14, which has recently been synthesised (V. Mascitti and E. J. Corey, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 15664). A glycerol diether containing ladderane and tetradecyl moieties 15 has been isolated from the anammox bacteria Scalindua species (J. S. S. Damasté et al., Chem. Commun., 2004, 2590). An enzyme preparation from cultured cells of Cryptomeria japonica catalyses the conversion of 4-coumaryl 4-coumarate 16 into the heartwood norlignan hinokiresinol 17 (T. Umezawa and co-workers, Chem. Commun., 2004, 2838). The proposed stereochemistry of dipiperamide A, isolated from white pepper (Piper nigrum), has been revised to that proposed for dipiperamide B 18 on the basis of unambiguous total synthesis (C. Kibayashi and co-workers, Tetrahedron Lett., 2004, 45, 57). The structure of dipiperamide B now needs to be revised.
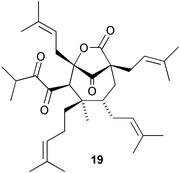
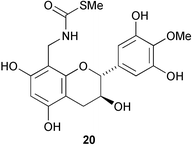
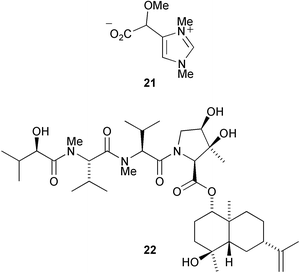
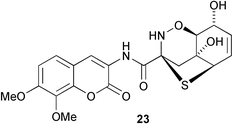
The phloroglucinol derivative perforatumone 19, from Hypericum perforatum, has a novel carbon skeleton (L. J. Harrison and co-workers, Tetrahedron Lett., 2004, 45, 9657). Glycosmis montana is the source of the first examples of flavonoids with a sulfur-containing amide moiety such as glymontanine A 20 (X. Hao and co-workers, Tetrahedron Lett., 2005, 46, 169). The main nematocidal agent present in an Australian marine sponge of the genus Echinodictyum has been identified as the betaine echinobetaine B 21 (R. J. Capon et al., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2005, 3, 118). The “blackleg” fungus Leptospaeria maculans (Phoma lingam) produces a highly selective phytotoxin depsilairidin 22, a sesquiterpenoid depsipeptide containing the novel amino acid 3,4-dihydroxy-3-methylproline (M. S. C. Pedras et al., Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 4615). Aspergillazine A 23 is one of a series of metabolites of Aspergillus unilateralis that contain unusual heterocyclic systems (R. J. Capon et al., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2005, 3, 123).
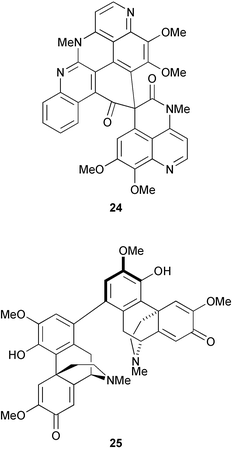
The structure of the spiro polycyclic aromatic alkaloid lihouidine 24, from marine sponge of the genus Suberea, was established by X-ray analysis (B. F. Bowden et al., J. Org. Chem., 2004, 69, 7791). The dimeric morphine alkaloids saludimerine A 25 and its atropisomer, saludimerine B, have been isolated from Croton flavens (G. Bringmann and co-workers, J. Org. Chem., 2004, 69, 8602). Saludimerines A 25 and B are configurationally stable at room temperature but slowly interconvert in methanol over several days.
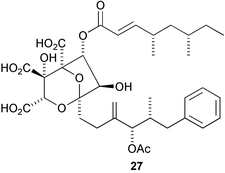
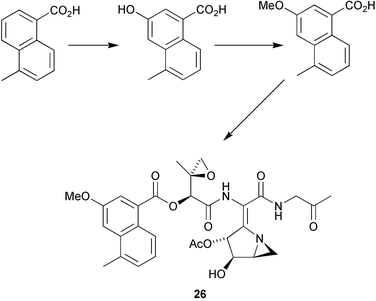
The biosynthesis of the naphthoate fragment of the antitumour antibiotic azinomycin A 26 has been studied using labelled naphthoate precursors (P. A. S. Lowden and co-workers, Chem. Commun., 2004, 2600). Earlier studies had demonstrated the polyketide nature of the naphthoate ring system. This study has demonstrated that the oxygen is introduced by a P450-type oxidation and that the oxygen is methylated prior to attachment to the rest of the azinomycin skeleton (Scheme 1). R. J. Cox and co-workers have used PCR primers for the rapid cloning and expression of a fungal polyketide gene involved in squalestatin S1 27 biosynthesis (Chem. Commun., 2004, 2260). Using a C-MeT specific probe allowed the cloning of a synthase gene which, when expressed, led to the biosynthesis of the tetraketide side chain of squalestatin S1 27. Sulfatases are enzymes that catalyse the cleavage of sulfate esters in biological systems. The mechanism and biological importance of sulfatases have been reviewed by C.-H. Wong and co-workers (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 5736).
 | ||
| Scheme 1 | ||
Studies by the research group of C. P. Whitman have demonstrated the unusual hydratase activity of malonate semialdehyde decarboxylase (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 15658). Incubation of the enzyme with 2-oxo-3-pentynoate resulted in the isolation of acetopyruvate leading the authors to speculate on the evolutionary origin of this enzyme (Scheme 2). K. C. Brown and co-workers have developed a new approach for the cell-specific delivery of a chemotherapeutic to lung cancer cells (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 15656). Attaching a cancer-targeting peptide to a chemotherapeutic allows these new conjugates to discriminate between cancerous and normal cells.
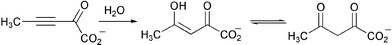 | ||
| Scheme 2 | ||
The redox processes of membrane-bound cytochrome c oxidase have been studied by attaching the protein to an electrode using a His-tag linker (P. Hildebrandt and co-workers, Chem. Commun., 2004, 2376). Surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy was then used to demonstrate the intact heme sites of the immobilised enzyme. J. A. Camarero and co-workers have demonstrated the use of expressed protein ligation (EPL) for the preparation of arrays of proteins covalently attached to a modified glass surface (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 14730). The proteins are linked to the surface using a stable peptide bond while still retaining their folded state and biological activity.
Z. Yang and B. Xu have developed a simple visual assay for screening the activities of enzyme inhibitors based on the hydrogelation of small molecules (Chem. Commun., 2004, 2424). A. J. Walker and N. C. Bruce have studied the effect of increasing the hydrophilicity of ionic liquids for co-factor dependent enzyme catalysis (Chem. Commun., 2004, 2570). They found that a moderately hydrophilic cation with a hydrophobic anion was capable of supporting the activity of the NADP+ dependent morphine dehydrogenase.
The recent developments of lipase mediated kinetic resolution of racemates in organic solvents have been reviewed (A. Ghanem and H. Y. Aboul-Enein, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2004, 15, 3331). T. Matsuda and co-workers have generated a continuous-flow supercritical CO2 process for the kinetic resolution of racemic alcohols with an immobilized lipase (Chem. Commun., 2004, 2286). Using this process allows the quantitative isolation of the corresponding optically active alcohols and acetates with up to 99% e.e. (Scheme 3). M. T. Reetz and W. Wiesenhöfer have also developed a process for the kinetic resolution of alcohols using supercritical CO2 (Chem. Commun., 2004, 2750). This involves a biphasic system composed of poly(ethylene glycol)/scCO2 which can be used either as a batch or continuous flow process.
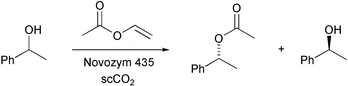 | ||
| Scheme 3 | ||
A. Kamal and G. Chouhan have enhanced the enantioselectivity of the lipase catalysed resolution of 1,2-diols using the ionic liquid, [bmim]PF6 as the reaction medium (Tetrahedron Lett., 2004, 45, 8801). Employing immobilised enzyme from Pseudomonas cepacia gave very high conversions and typical e.e. values around 99%. A new approach for the synthesis of aryl-hydroxylamines has been reported by the chemoselective reduction of the aromatic nitro compound using bakers' yeast (J. Cui and co-workers, Chem. Commun., 2004, 2338). Aromatic compounds bearing electron-withdrawing groups gave excellent conversions under these mild conditions (Scheme 4).
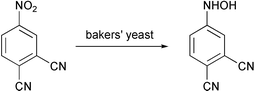 | ||
| Scheme 4 | ||
J. C. Spain and co-workers have investigated bacterial monooxygenases for the regiospecific single-step hydroxylation of diphenylacetylene (DPA) (Chem. Commun., 2004, 2402). This biotransformation of DPA using recombinant strains expressing various toluene monooxygenases, was capable of producing either meta- or para-hydroxydiphenylacetylene. R. A. Field and co-workers have identified straightforward enzymatic and chemo-enzymatic approaches to uridine diphospho sugars (Chem. Commun., 2004, 2706). Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase used to effect the key transformation showed a surprisingly broad substrate specificity.
M. Larchevêque and co-workers have demonstrated the use of lipase from Burkholderia cepacia for the kinetic resolution of cyclic N-Boc protected β-amino esters (Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2004, 15, 3407). Both 5- and 6-membered ring systems were successfully resolved to give the corresponding acids and esters in excellent enantiomeric excess (Scheme 5).
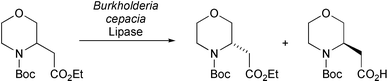 | ||
| Scheme 5 | ||
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2005 |