Organic mixed valence compounds with N,N-dihydrodimethylphenazine redox centres
Abstract
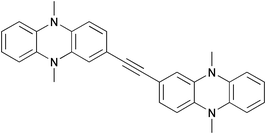
The mixed-valence character of four bis(N,N-dihydrodimethylphenazine) radical cation derivatives with varying π-electron bridges was investigated. The electron transfer (ET) distance within these derivatives varies from ca. 12.5 Å for 1,2-bis[2-(5,10-dihydro-5,10-dimethylphenazinyl)]acetylene (1) to ca. 19.3 Å for 9,10-bis[2-(5,10-dihydro-5,10-dimethylphenazinyl)ethynyl]anthracene (4). All radical cation species show intense intervalence charge-transfer (IV-CT) bands in the NIR. The Mulliken–Hush analysis was used to derive the electronic coupling V, which ranges from 310 to 870 cm−1. Comparisons with analogous ET systems in which the dihydrodimethylphenazine redox centres have been replaced by triarylamine units show that the dihydrodimethylphenazine species have a significantly higher internal reorganisation energy associated with the ET. This behaviour is attributed to C–N stretching and C–C ring modes of the dihydrodimethylphenazine units.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...