Monoclonal-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunochromatographic assay for enrofloxacin in biological matrices
Hiroo
Watanabe
*,
Atsuko
Satake
,
Yasumasa
Kido
and
Akio
Tsuji
Research Institute for Animal Science in Biochemistry and Toxicology, 3-7-11, Hashimotodai, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 229-1132, Japan
First published on 13th December 2001
Abstract
Enrofloxacin has been increasingly used in veterinary medicine to treat microbial infections. A simple and reliable analytical method for this drug is required. The current determination by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is sensitive but labor-intensive. This paper reports an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using a monoclonal antibody (MAb) and the development of a rapid test kit based on immunochromatography. The detection limits using the ELISA were 10 ppb for chicken liver and muscle, and 1 ppb for cattle milk, respectively. The mean recovery values were 77.3–96.0% for chicken liver, 72.4–92.0% for chicken muscle and 84.0–99.0% for cattle milk. The detection limits using the kit were ca. 100 ppb for chicken muscle and ca. 10 ppb for cattle milk, respectively. All ELISA results for assay of chicken liver, chicken muscle and cattle milk were confirmed using HPLC which is used as the routine assay. The HPLC (x) and ELISA (y) results showed close correlation for chicken liver (y = 8.7 + 0.85x, r2 = 0.99, n = 25), chicken muscle (y = −3.9 + 0.94x, r2 = 0.98, n = 25) and cattle milk (y = 18.4 + 0.92x, r2 = 0.99, n = 25).
Introduction
Infectious diseases are a serious problem for the livestock industries; therefore, various kinds of antibiotics and synthetic antibacterials are widely used for prevention and treatment. The fluoroquinolones are the most important group of synthetic antibacterials. Enrofloxacin, benofloxacin, danofloxacin and ofloxacin belong to this group and enrofloxacin is particularly used to treat livestock in Japan (Fig. 1). In Japan, according to the Japanese Food Sanitation Law established in 1947, food should not contain antibiotics or synthetic antibacterial agents. However, in January 1994, the Ministry of Health and Welfare required the Food Hygiene Investigative Committee to determine maximum residue limits (MRLs) for antibiotics and antibacterial agents. Until 2000, the MRLs of several substances (benzylpenicillin, oxytetracycline, carbadox, trenbolone, zeranol, closantel, flubendazole, ivermectin and so on) were decided, but the MRL for enrofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones have not been determined. On the other hand, the species of animal, usage, dosage and withdrawal period for enrofloxacin have been provided by the Regulation for Usage of Veterinary Medicines (The Ministry Ordinance of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fishers, No. 67, 5.31, 2000). In Europe, the European Commission, Regulation 2377/90 and its successive regulations, has established the Maximum Residue Limits (MRL) for drugs employed in veterinary medicine. The MRL has been stated at 30 μg kg−1 for the sum of enrofloxacin and its active metabolite (ciprofloxacin) for muscle tissue. In Japan, residual antibacterials presently causing food sanitation problems are the unchanged parent compounds administered to livestock. In order to monitor enrofloxacin residue levels in livestock products, simple and rapid analytical methods are required. Various analytical methods, such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),1–5 liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS),6,7 LC-MS-MS,8–12 and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)13,14 have been reported. Among these, ELISA is the most suitable method for rapid screening of enrofloxacin residues in the veterinary field. In this study, we have aimed to prepare anti-enrofloxacin monoclonal antibody (MAb) and ELISAs using horseradish peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase as the label enzyme. We have also applied the ELISA to determination of enrofloxacin in chicken liver, chicken muscle and cattle milk, and developed a rapid screening test kit based on an immunochromatographic method for monitoring enrofloxacin residues in chicken liver, chicken muscle and cattle milk. | ||
| Fig. 1 Structures of enrofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, benzofloxacin, danofloxacin and ofloxacin. | ||
Experimental
Chemicals
Enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin were supplied by Bayer Japan (Tokyo, Japan). Danofloxacin was supplied by Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (Tokyo, Japan). Benofloxacin and ofloxacin were supplied by Takeda Pharmaceuticals (Osaka, Japan) and Daiichi Pharmaceuticals (Tokyo, Japan), respectively. Human serum albumin (HSA) and ovalbumin (OVA) were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). Freund’s complete and incomplete adjuvants were obtained from Nacalai Tesque (Kyoto, Japan). AffiniPure goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) and peroxidase-conjugated AffiniPure goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) were obtained from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories (West Grove, PA, USA). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (EIA grade) were obtained from Roche diagnostics (Mannheim, Germany) and immunoassay substrate kits, tetramethylbenzidine and p-nitrophenyl phosphate, from Bio-Rad Laboratories (Hercules, CA, USA). Block Ace was obtained from Dainippon Pharmaceuticals (Osaka, Japan). 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (WSC) was obtained from Dojindo laboratories (Kumamoto, Japan). Mouse monoclonal antibody isotyping kit was obtained from Amersham Pharmacia Biotech (Uppsala, Sweden). All other chemicals were obtained from Wako (Osaka, Japan).Buffers
Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (PBS) contained 0.2 g of KCl, 0.2 g of KH2PO4, 8 g of NaCl and 1.15 g of Na2HPO4 per litre of H2O. The HRP assay buffer contained 0.05% of Tween 20 and 25% of Block Ace in PBS. The ALP assay buffer contained 0.05% of Tween 20, 25% of Block Ace, 75 mM TRIS-HCl (pH 7.0), 1 mM MgCl2 and 0.1 mM ZnCl2 in PBS. The washing buffer contained 0.05% of Tween 20 and 0.9% of NaCl. The coating buffer contained 15 mM Na2CO3 and 35 mM NaHCO3.Apparatus
EIA plates (Falcon EIA Plate, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), plate washer (Delfia plate wash, Wallac, Turku, Finland) and plate reader (iEMS Analyzer, Labsystems, Finland) were used for the ELISA. The HPLC system consisted of a Shimadzu LC-10 system (Kyoto, Japan), equipped with a model 821-FP intelligent fluorescence detector (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan) operated at an excitation wavelength of 290 nm and an emission wavelength of 455 nm, and a Chromatopak C-R4A data system (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The separation was performed on an Inertsil C8 column (250 × 4.6 mm id, GL Science, Tokyo, Japan) with acetonitrile–0.05 M citric acid (8:92, w/w) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.0 ml min−1. The chromatograph was operated at 40 °C.Preparation of enrofloxacin–human serum albumin (enrofloxacin–HSA) conjugate and enrofloxacin–ovalbumin (enrofloxacin–OVA) conjugate
Enrofloxacin–HSA conjugate used for the immunogen was prepared according to the N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (NHS) method.15 Briefly, enrofloxacin (20 mg), NHS (10 mg) and WSC (12.5 mg) were dissolved in dimethylformamide (DMF, 1 ml) and the solution was stirred for 24 h at room temperature. The reactant solution was added dropwise to the HSA solution (50 mg in 3 ml PBS). The solution was stirred at room temperature for 3 h and dialyzed two times against H2O (3 l) and lyophilized. Enrofloxacin–OVA conjugate used for solid phase antigen was also prepared by the same manner.Immunization
The enrofloxacin–HSA conjugate (10 mg) was dissolved in PBS (10 ml) and 1 ml of it was emulsified with an equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant. Eight-weeks-old BALB/c mice were injected intraperitoneally with 300 μl of the emulsion. Two weeks later, the animals were boosted intraperitoneally with the same dose in Freund’s incomplete adjuvant every other week. After 3 weeks, the mice were bled and the titres of the antisera were determined by ELISA using enrofloxacin–OVA conjugate as an immobilised antigen. The mouse giving the highest titre was selected for fusion.Preparations of enrofloxacin–horseradish peroxidase (enrofloxacin–HRP) conjugate and enrofloxacin–alkaline phosphatase (enrofloxacin–ALP) conjugate
The enrofloxacin–enzyme conjugates were also prepared by the NHS method using the reaction mixture of enrofloxacin: enzyme (HRP or ALP) molar ratio (20∶1). The reaction mixture was purified from low molecular weight components by gel filtration using a Sephadex G-25 column (25 × 2.5 cm id). The absorbance at 280 nm and enzyme activity of each fraction was measured. The immunoreactivity of each fraction was also assayed by the ELISA described below. The highly immunoreactive fractions were stored at −80 °C until used.Production of monoclonal antibody
Spleen cells were fused with P3X63Ag8U.1 at a ratio of 3∶1 according to the standard procedure.16 Cells were plated at a density of 105 cells per well in 96 well, flat-bottomed microtitre plates. Hybridoma from wells having a positive response in the ELISA described below were cloned twice by limiting dilution and expanded. The class and subclass of the isotypes of the secreted antibody were determined by using a mouse monoclonal antibody isotyping kit. Anti-enrofloxacin MAb was purified from ascites fluid using an immobilised protein A column.ELISAs for measuring antibody titre and screening
The enrofloxacin–OVA conjugate was diluted (to 10 μg ml−1) in PBS and 100 μl of solution were added to each well of the microtitre plates and stored at 4 °C overnight. The solution was then discarded and 300 μl of 1% gelatin solution were added to each well. After 2 h of incubation at room temperature, the solution was discarded and the plates were washed three times with the washing buffer. For the assay, 50 μl of diluted mice antisera or tissue culture supernatants were pipetted into a well of the microtitre plate coated with enrofloxacin–OVA conjugate and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. The plates were then washed three times with the washing buffer. This was followed by the addition of 50 μl of peroxidase-conjugated AffiniPure goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) diluted in HRP assay buffer (0.16 μg ml−1 IgG). After incubation for 1 h at 37 °C, the plates were washed three times with the washing buffer. The HRP substrate solution (100 μl) was dispensed into each well. After incubation for 30 min at 37 °C, adding 100 μl of 0.5 M H2SO4 terminated the enzyme reaction. The absorbance at 450 nm was determined in a microtitre plate reader (iEMS Analyzer).ELISA using HRP as label
The ELISA system was constructed by the same manner described in the previous reports.17,18 The second antibody was immobilised on the well of the microtitre plates by the addition of 100 μl of AffiniPure goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) solution (10 μg ml−1) in coating buffer per well. After standing overnight at 4 °C, the solution was discarded and then 300 μl of 1% gelatin solution were added to the well. After washing five times with 300 μl of washing buffer, 50 μl of the MAb solution diluted with assay buffer (0.2 μg ml−1 MAb), 100 μl of the standard or sample solutions, then 50 μl of enrofloxacin–HRP conjugate solution diluted with HRP assay buffer (1.0 μg ml−1) were added to the well and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. After washing five times, 100 μl of HRP substrate solution were added to the well and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. Then, 100 μl of 0.5 M H2SO4 were added to stop the reaction and the absorbance was measured at 450 nm.Preparations of spiked chicken tissue samples
Enrofloxacin solutions to be used for chicken tissue spiking were prepared in methanol at each of the following concentrations: 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16 μg ml−1. Each 1 g of minced liver or muscle of chicken was spiked with 50 μl each of the above solutions to give tissue concentrations of 50, 100, 200, 400 and 800 ng g−1.Preparations of spiked cattle milk samples
Enrofloxacin solutions to be used for cattle milk spiking were prepared in methanol at each of the following concentrations: 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16 μg ml−1. Each 1 ml of cattle milk was spiked with 50 μl each of the above solutions to give cattle milk concentrations of 50, 100, 200, 400 and 800 ng ml−1.Preparations of samples for ELISA
Minced chicken liver and muscle (1 g) was homogenized with 10 ml of methanol–PBS (pH 4) (80:20, v/v). After centrifugation at 2800 rpm for 10 min, 100 μl of supernatant was diluted with HRP assay buffer to 1 ml (total 100-fold dilution) prior to ELISA analysis. Cattle milk (100 μl) was diluted to 1 ml with HRP assay buffer (total 10-fold dilution) and assayed.ELISA using ALP as label
The ELISA using ALP as the label enzyme was run essentially as described above. To the second antibody coated plates, 50 μl of the diluted MAb solution (0.4 μg ml−1 MAb), 100 μl of the standard or sample solution and 50 μl of the enrofloxacin–ALP conjugate solution (6.0 μg ml−1 ALP) were added and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. The subsequent steps were the same as described for the ELISA using HRP, except that enzyme activity was measured with the immunoassay substrate kit for ALP.Preparation of immunochromatographic test kit
The test kit was prepared by using the same device in the previous reports.17,18 As shown in Fig. 2, the equipment is composed of four parts, substrate and developing solution part (A), ALP–conjugate part (B), colour developing part (immobilised monoclonal antibody) (C) and absorption part (D). The substrate for ALP, sodium 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate, is absorbed in A. The developing solution (0.1 M N-cyclohehyl-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid–HCl buffer containing 1M MgCl2) is contained in the developing solution reservoir. The ALP-conjugate is absorbed in B. D contains the adsorbent pad.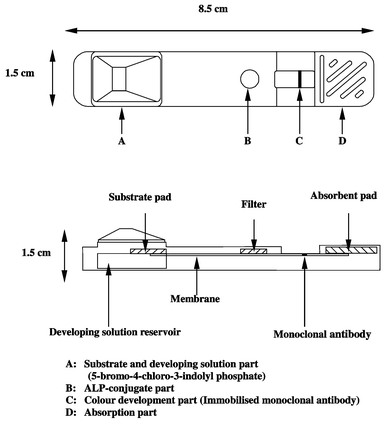 | ||
| Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of immunochromatograph. | ||
Sample preparations of chicken liver and muscle for rapid test kit
Minced tissue (2 g) was homogenized with 5 ml of ALP assay buffer. After centrifugation at 2800 rpm for 10 min, 100 μl of supernatant was diluted with ALP assay buffer to 1 ml (total 25-fold dilution) prior to rapid test analysis.Sample preparation of cattle milk for rapid test kit
Cattle milk was diluted 2-fold with ALP assay buffer prior to rapid test analysis.Sample preparations of chicken liver and muscle for HPLC
Minced tissue (2 g) was homogenized with 40 ml of acetonitrile. The homogenate was centrifuged at 2800 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was decanted into 50 ml glass centrifuge tubes and 20 ml of n-hexane was added. The sample was shaken on a shaker for 10 min and centrifuged at 2800 rpm for 10 min, and the lower layer was evaporated. The residue was dissolved in 4 ml of mobile phase and filtered thorough a Millex-LH 0.45 μm filter (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA) prior to HPLC analysis. A 20 μl volume of the solution was injected onto the HPLC systems.Rapid test for enrofloxacin in chicken liver, chicken muscle and cattle milk
One drop (about 50 μl) of the sample solution was spotted on part B and then part A was added immediately. The developing solution migrated upward while dissolving the substrate. The enrofloxacin–ALP conjugate captured on immobilised MAb, reacted with the substrate (BCIP) and developed a blue colour line on part C after 10–20 min. The colour intensity decreased with increasing concentration of enrofloxacin in the sample solution and was compared with that of a standard solution.Results and discussion
Establishment of hybridoma
Enrofloxacin was coupled to carrier protein (HSA) via the carboxylic acid moiety to make it an immunogen. This enrofloxacin–HSA conjugate was used to immunize BALB/c mice. Spleen cells from the mice immunized with enrofloxacin–HSA were fused with P3X63Ag8U.1 myeloma cells and the resulting hybridomas were selected in HAT medium. One or more growing hybridomas were observed in almost all wells at 10 d. The supernatant from each of wells was screened for antibodies against enrofloxacin by an indirect ELISA using microtitre plates coated with enrofloxacin–OVA conjugate. The cells from this well showing the strongest response was tested again in a competitive ELISA for their ability to recognize unconjugated (free) enrofloxacin. Only one well gave positive signals in both screenings. This hybridoma was cloned twice by limiting dilution to guarantee their monoclonal origin. After cell culture, the cultured hybridoma was intraperitoneally injected to mice. The MAb was purified by affinity chromatography using a protein A column.Characterization of monoclonal antibody
The MAb was characterized by using a culture supernatant of this clone. The subclass of the MAb was identified as IgG1 and the light chain as kappa chain. The MAb was also obtained from the ascites fluid of mice. The titre of the purified ascites fluid was more than 80 000. The representative ELISA working curve is shown in Fig. 3. The cross-reactivities of the MAb were also examined. The antibody is highly specific for enrofloxacin and showed no cross-reactivity with other fluoroquinolones [ciprofloxacin, benofloxacin, danofloxacin and ofloxacin (<0.003%)]. Other antibiotics (ampicillin, avilamycin, avoparcin, bacitracin, benzylpenicillin, cefazolin, colistin, dihydrostreptomycin, erythromycin, fosfomycin, fradiomycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, lasalocid, monensin, nosiheptide, oxytetracycline, salinomycin, semduramicin and spectinomycin) have no cross-reactivity to the MAb (<0.001%). | ||
| Fig. 3 Working curves for enrofloxacin in chicken liver, chicken muscle and cattle milk. | ||
ELISAs for enrofloxacin using HRP and ALP as the label enzyme
The typical working curve for the competitive ELISA using enrofloxacin–HRP conjugate is shown in Fig. 3. The working range of the assay was determined as 0.01–5 ng per well (0.1–50 ng ml−1). The mean midpoint of the standard curve (n = 8) was calculated as 1.2 ng ml−1 (0.12 ng per well). The detection limit was 0.1 ng ml−1, which was determined as the mean of the B0 - 3s (n = 8). To elucidate the variability of the standard curves for different assays, ten standard solutions (0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.1, 6.3, 12.5, 25, 50 ng ml−1) were prepared independently with assay buffer and analyzed by the ELISA method. The intra- and inter-assay variations ranged from 0.4 to 8.5% (n = 8) and from 0.5 to 10.4% (n = 3), respectively. The ELISA of enrofloxacin using ALP as label enzyme was also developed for the rapid test kit. The working range of the assay was 0.1–50 ng ml−1. The IC50 of the standard curve (n = 8) was 2 ng ml−1. The detection limit was 0.1 ng ml−1. The intra- and inter-assay variations ranged from 0.7 to 3.8% (n = 8) and from 0.7 to 5.4% (n = 3), respectively.ELISAs for enrofloxacin in chicken liver, chicken muscle and cattle milk
ELISAs are usually influenced by the components in biological matrices. To elucidate the influence of biological matrices on the assay of enrofloxacin, various dilutions of biological matrices were examined. When sample spiked with enrofloxacin were diluted 100-fold for tissues and 10-fold for cattle milk with HRP assay buffer, the B/B0% values at each concentration of diluted samples were almost same as those of the assay buffer standard solutions in HRP assay buffer (Fig. 3). The measurable range was 10–5000 ng g−1 (10–5000 ppb) for chicken tissues and 1–500 ng ml−1 (1–500 ppb) for cattle milk. The intra- and inter-assay variations are summarized in Tables 1–3.| Enrofloxacin (ppb) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | ||
| Intra-assay variation (n = 5) | ||||||
| Day 1 | Mean recovery (%) | 80.4 | 84.0 | 85.0 | 84.5 | 82.5 |
| s (%) | 7.8 | 7.1 | 9.4 | 6.2 | 6.2 | |
| RSD (%) | 9.7 | 8.5 | 11.0 | 7.4 | 7.5 | |
| Day 2 | Mean recovery (%) | 96.0 | 80.6 | 82.0 | 76.5 | 77.3 |
| s (%) | 8.9 | 4.0 | 7.6 | 4.9 | 4.6 | |
| RSD. (%) | 9.3 | 4.9 | 9.2 | 6.4 | 5.9 | |
| Day 3 | Mean recovery (%) | 93.2 | 83.2 | 85.0 | 83.0 | 80.8 |
| s (%) | 8.2 | 8.9 | 7.9 | 5.7 | 3.6 | |
| RSD. (%) | 8.8 | 10.7 | 9.3 | 6.9 | 4.5 | |
| Inter-assay variation (n = 3) | ||||||
| Mean recovery (%) | 89.9 | 82.6 | 84.0 | 81.3 | 80.2 | |
| s (%) | 10.4 | 6.6 | 7.8 | 6.3 | 5.1 | |
| RSD (%) | 11.6 | 8.0 | 9.3 | 7.8 | 6.3 | |
| Enrofloxacin (ppb) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | ||
| Intra-assay variation (n = 5) | ||||||
| Day 1 | Mean recovery (%) | 72.4 | 78.4 | 80.0 | 77.0 | 75.5 |
| s (%) | 3.3 | 8.2 | 6.1 | 5.7 | 3.6 | |
| RSD (%) | 4.5 | 10.4 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 4.8 | |
| Day 2 | Mean recovery (%) | 92.0 | 88.2 | 87.0 | 82.0 | 87.3 |
| s (%) | 11.7 | 5.4 | 8.4 | 11.5 | 9.7 | |
| RSD (%) | 12.8 | 6.1 | 9.6 | 14.0 | 11.1 | |
| Day 3 | Mean recovery (%) | 80.4 | 79.0 | 84.0 | 76.0 | 81.0 |
| s (%) | 6.5 | 5.4 | 4.2 | 2.2 | 3.5 | |
| RSD (%) | 8.1 | 6.8 | 5.0 | 2.9 | 4.3 | |
| Inter-assay variation (n = 3) | ||||||
| Mean recovery (%) | 81.6 | 81.9 | 83.7 | 78.3 | 81.3 | |
| s (%) | 11.1 | 7.6 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 7.7 | |
| RSD (%) | 13.7 | 9.2 | 8.0 | 9.5 | 9.4 | |
| Enrofloxacin (ppb) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | ||
| Intra-assay variation (n = 5) | ||||||
| Day 1 | Mean recovery (%) | 84.0 | 88.0 | 95.0 | 96.0 | 95.0 |
| s (%) | 9.4 | 11.0 | 7.1 | 5.8 | 6.8 | |
| RSD (%) | 11.2 | 12.4 | 7.4 | 6.0 | 7.2 | |
| Day 2 | Mean recovery (%) | 97.2 | 94.8 | 94.0 | 95.0 | 91.0 |
| s (%) | 6.3 | 5.0 | 8.2 | 9.4 | 8.4 | |
| RSD (%) | 6.4 | 5.3 | 8.7 | 9.8 | 9.2 | |
| Day 3 | Mean recovery (%) | 90.0 | 88.8 | 96.0 | 99.0 | 95.0 |
| s (%) | 10.0 | 11.7 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 6.8 | |
| RSD (%) | 11.1 | 13.2 | 6.8 | 2.3 | 7.2 | |
| Inter-assay variation (n = 3) | ||||||
| Mean recovery (%) | 90.4 | 90.5 | 95.0 | 96.7 | 93.7 | |
| s (%) | 9.8 | 9.5 | 6.8 | 6.2 | 7.1 | |
| RSD (%) | 10.8 | 10.5 | 7.2 | 6.5 | 7.6 | |
Rapid test for enrofloxacin in chicken liver, chicken muscle and cattle milk
The amount of sample solution was examined and the appropriate sample volume was found to be ca. 50 μl (equivalent to 1 drop). When undiluted milk samples were tested, they took a long time to be completely absorbed into the part B because of their viscosity and the colour did not develop. From the results of dilution with ALP assay buffer, 2-fold dilution gave the clear colouration for cattle milk. The lower detection limit (LDL) is defined here as the concentration of enrofloxacin in the sample solution that just distinguished visibility with the colouration of the blank. A typical result is shown in Table 4. LDLs were 50 ppb for cattle milk as well as the standard solution, and 100 ppb for chicken muscle. When chicken liver was assayed, the colour developing part turned blue entirely and the clear blue line did not appear. It seems that some interfering substances to the ALP detection system exists in the liver extract. A clean-up treatment must be added.| Sample | Concentration of enrofloxacin (ppb) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 10 | 50 | 100 | |||
| a Clearly distinguishable. b Impossible to detect. | |||||||
| Buffer | +++ | ++ | + | >a | — | — | |
| Chicken liverb | |||||||
| Chicken muscle | ++ | + | > | — | |||
| Cattle milk | ++ | ++ | ++ | > | — | — | |
Comparison of ELISA with HPLC
To evaluate the validation of the ELISA, chicken liver, chicken muscle, and cattle milk spiked with various amounts of enrofloxacin were analysed by HPLC and ELISA. In order to avoid the matrix effect for the HPLC, the samples were cleaned-up. In ELISA, the samples were diluted with HRP assay buffer and assayed. The correlation between both methods is shown in Table 5.Conclusion
The ELISA and Rapid Test has been shown to be capable of detecting enrofloxacin residues in a range of edible tissues. The inability of the procedures to detect ciprofloxacin residues render the procedures unsuitable for routine use in Europe. As the regulations stand in Japan presently for antibiotic monitoring both tests fulfill the analytical requirements. However if the Japanese MRL follows the criteria similar to that laid down in Europe the assays may find limited use from a regulatory stance.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants-in-aid from the Bio-Oriented Technology Research Advancement Institute of Japan. The authors wish to acknowledge Fujirebio Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) for supplying the immunochromatographic test kit.References
- M. Horie, K. Saito, N. Nose and H. Nakazawa, J. Chromatogr., B: Biomed. Appl., 1994, 653, 69 Search PubMed.
- J. Manceus, M. Gicquel, M. Laurentie and P. Sanders, J. Chromatogr., B: Biomed. Appl., 1999, 726, 175 Search PubMed.
- M. A. Garcia, C. Solans, J. J. Aramayano, S. Rueda, M. A. Bregante and A. de Jong, Biomed. Chromatogr., 1999, 13, 350 CrossRef CAS.
- P. G. Gigosos, P. R. Revesado, O. Cadahia, C. A. Fente, B. I. Vazquez, C. M. Franco and A. Cepeda, J. Chromatogr., A, 2000, 871, 31 CrossRef CAS.
- J. C. Yorke and P. Froc, J. Chromatogr., A, 2000, 882, 63 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Delepine, D. Hurtaud-Pessel and P. Sanders, Analyst, 1998, 123, 2743 RSC.
- S. B. Turnipseed, C. C. Walker, J. E. Roybal , A. P. Pfenning and J. A. Hurlbut, J. AOAC Int., 1998, 81, 554 Search PubMed.
- R. P. Schneider, J. F. Ericson, M. J. Lynch and H. G. Fouda, Biol. Mass Spectrom., 1993, 22, 595 Search PubMed.
- D. R. Doerge and S. Bajic, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 1995, 9, 1012 CAS.
- J. B. Schilling, S. P. Cepa, S. D. Menacherry, L. T. Bavda, B. M. Heard and B. L. Stockwell, Anal. Chem., 1996, 68, 1905 CrossRef CAS.
- D. A. Volmer, B. Mansoori and S. J. Locke, Anal. Chem., 1997, 69, 4143 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Delepine and D. Hurtaud-Pessel, in Proceedings of the Euroresidue IV conference, Veldhoven, The Netherlands, May 8–10, 2000, ed. L. A. van Ginkel and A. Ruiter, Federation of European Chemical Societies (FECS), pp. 350–355 Search PubMed.
- P. Hammer and W. Heeschen, Milchwissenschaft, 1995, 50, 513 Search PubMed.
- C. K. Holtzapple, S. A. Buckley and L. H. Stanker, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1997, 45, 1984 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Tijissen, Practice and Theory of Enzyme Immunoassays, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1985, pp. 283–285 Search PubMed.
- M. Köhler and C. Milstein, Nature (London), 1975, 256, 495.
- H. Watanabe, A. Satake, M. Matsumoto, Y. Kido, A. Tsuji, K. Ito and M. Maeda, Analyst, 1998, 123, 2573 RSC.
- H. Watanabe, A. Satake, Y. Kido and A. Tsuji, Analyst, 1999, 124, 1611 RSC.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2002 |
