Third-order nonlinear optical properties of carboxyl group dominant carbon nanodots†
Abstract
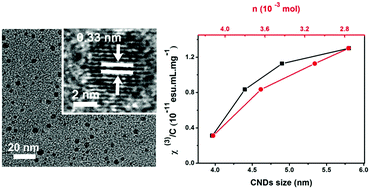
We quantitatively investigate the nonlinear optical (NLO) property of carbon nanodots (CNDs, less than 10 nm) by the Z-scan technique using a tunable 532 nm nanosecond laser system. These CNDs were fabricated by an electrochemical etching method from graphite rods. Our results suggested that the third-order nonlinear susceptibility χ(3) of CNDs is strongly dependent on the diameter of the CNDs apparently; the nonlinear refractive index γ decreased as the size of CNDs decreased, while the nonlinear absorption coefficient β showed an opposite tendency to γ. We further demonstrated that the carboxyl group on the CND surface plays a key role and has significant impact on the third-order nonlinear susceptibility χ(3).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...