Preparation and characterization of double macromolecular network (DMMN) hydrogels based on hyaluronan and high molecular weight poly(ethylene glycol)†
Abstract
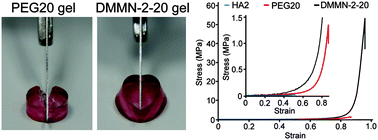
Abundant research efforts have been devoted to meet the demands for high-strength hydrogels in biomedical applications. Double-network (DN) hydrogels and homogeneous hydrogels are two typical samples. In this study, a novel ultra-strong and resilient double macromolecular network (DMMN) hydrogel system has been developed via a two-step sequential cross-linking process using hyaluronan (HA) and high molecular weight poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) for the first and second network, respectively. A lower concentration of the HA precursor solution and a higher concentration of the PEG precursor solution as well as a higher molecular weight of the PEG precursor are beneficial to produce high-strength DMMN gels. Dynamic light scattering measurements demonstrate that DMMN gels possess the more evenly distributed polymer networks; the distinctive double and relatively evenly distributed networks of the DMMN gel make it combine the current DN and homogeneous network strategies for preparing robust hydrogels. The optimized DMMN gel is capable of sustaining up to 50 MPa of compressive stress. Besides, DMMN gels exhibit excellent cytocompatibility. This study expands the DN principle in designing and fabricating high-strength hydrogels with biocompatible macromolecules that show a promising prospect for biomedical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...