Chitosan scaffolds with a shape memory effect induced by hydration
Abstract
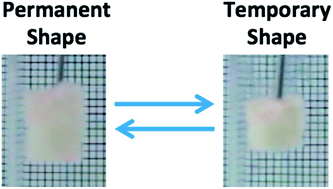
We demonstrate that chitosan-based porous scaffolds can present a shape memory effect triggered by hydration. The shape memory effect of non-crosslinked (CHT0) and genipin-crosslinked (CHT1) scaffolds was followed by innovative hydromechanical compressive tests and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), while the sample was immersed in varying compositions of water–ethanol mixtures. By dehydration with higher contents of ethanol, the vitreous-like nature of the amorphous component of chitosan allows the fixation of the temporary shape of the scaffold. The presence of water disrupts inter-molecular hydrogen bonds permitting large-scale segmental mobility of the chitosan chains upon the occurrence of glass transition and thus the recovery of the permanent shape of a pre-deformed scaffold. Results showed that chitosan possesses shape memory properties, characterized by a fixity ratio above 97.2% for CHT0 and above 99.2% for CHT1 and a recovery ratio above 70.5% for CHT0 and 98.5% for CHT1. In vitro drug delivery studies were also performed to demonstrate that such devices can also be loaded with molecules. We show that the developed chitosan scaffolds are candidates of biomaterials for applications in minimally invasive surgery for tissue regeneration or for drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...