Signal amplified two-dimensional photonic crystal biosensor immobilized with glyco-nanoparticles†
Abstract
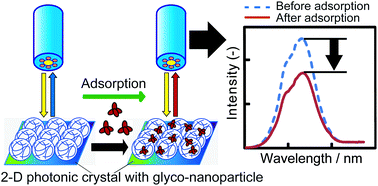
A two-dimensional, glycopolymer-immobilized, photonic crystal (PhC) biosensor was developed for the detection of proteins. Glycopolymers with different conformations, homopolymers and sugar-incorporating nanoparticles were immobilized on the PhC using intermediate succinimide-containing polymers and proteins. The surface modification was analyzed in detail, and the sugar–protein interaction was detected by monitoring changes in the reflection intensity that was expressed by the two-dimensional PhC. The surface modifications were performed successfully, and specific interactions were detected between the glycopolymers and the proteins. Stronger bonds were present between the glycopolymers and the target proteins than between the glycopolymers and the monovalent sugar, because of a clustering effect. The sugar-incorporating nanoparticles showed a larger binding capacity compared with the homopolymers, and low protein concentrations (with a detection limit of 6.0 ng mL−1) were detected using the sugar-incorporating nanoparticle-immobilized PhC. The detection limit of the developed biosensor was lower than that of surface plasmon resonance sensor (1.43 μg mL−1). The results of this study indicated the potential of the developed biosensor for the detection of a variety of biomolecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...