Synthesis, characterization and in vitro evaluation of novel vitamin D3 nanoparticles as a versatile platform for drug delivery in cancer therapy†
Abstract
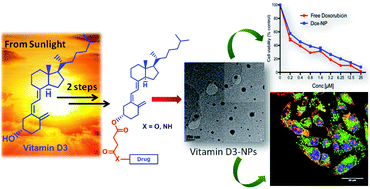
Development of novel nanotechnology based platforms can impact cancer therapeutics in a paradigm shifting manner. The major concerns in drug delivery in cancer therapy are the biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxic nature, easy and short synthesis and versatility of the nanovectors. Herein we report the engineering of versatile nanoparticles from biocompatible, biodegradable and non-toxic lipid soluble vitamin D3. We have conjugated different clinically used cytotoxic drugs (paclitaxel and doxorubicin) as well as PI3 kinase inhibitor (PI103) with vitamin D3 using a succinic acid linker. Sub-200 nm, monodispersed nanoparticles with high drug loading were engineered from the vitamin D3–succinic acid–drug conjugates. These nanoparticles released the active drugs at pH 5.5 in a slow and sustained manner over 100 h. Furthermore, these nanoparticles were taken up by HeLa cells into the low pH lysosomal compartments through an endocytosis mechanism in 6 h. Finally, these drug loaded vitamin D3 nanoparticles induced HeLa cervical cancer cell death in a dose dependent manner at 48 h to show their potential in cancer therapeutics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...