Electrochemical properties and morphological evolution of pitaya-like Sb@C microspheres as high-performance anode for sodium ion batteries†
Abstract
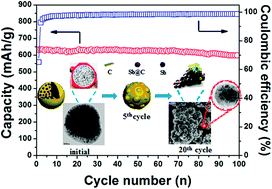
Pitaya-like Sb@C microspheres are prepared successfully by facile aerosol spray drying synthesis. Structural and morphological characterizations reveal that the Sb@C microspheres have a uniform pitaya-like structure, with well crystallized Sb nanoparticles embedded homogeneously in the carbon matrix. The Sb@C microsphere electrodes exhibit high Na storage capacity of 655 mA h g−1 at C/15 with excellent cyclability (93% of capacity retention over 100 cycles), as well as remarkable rate capability. Also, the morphological evolution of the Sb@C microspheres is unravelled to account for its excellent electrochemical performance, caused by maintenance of the pitaya-like configuration during cycling. This structural stability guarantees tight contact of Sb with carbon buffer, as well as uniform distribution of Sb to balance the localized mechanical stress, ensuring excellent electrochemical performance. The structural design and synthetic method reported in this work may provide an effective way to stabilize electrochemical performance of Na-storable alloy materials and therefore provide a new prospect for creation of cycle-stable alloy anodes for high capacity Na-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...