Efficient and selective DNA modification on bacterial membranes†
Abstract
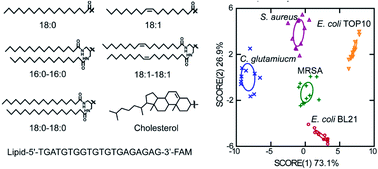
With highly precise self-assembly and programmability, DNA has been widely used as a versatile material in nanotechnology and synthetic biology. Recently, DNA-based nanostructures and devices have been engineered onto eukaryotic cell membranes for various exciting applications in the detection and regulation of cell functions. While in contrast, the potential of applying DNA nanotechnology for bacterial membrane studies is still largely underexplored, which is mainly due to the lack of tools to modify DNA on bacterial membranes. Herein, using lipid–DNA conjugates, we have developed a simple, fast, and highly efficient system to engineer bacterial membranes with designer DNA molecules. We have constructed a small library of synthetic lipids, conjugated with DNA oligonucleotides, and characterized their membrane insertion properties on various Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Simply after incubation, these lipid–DNA conjugates can be rapidly and efficiently inserted onto target bacterial membranes. Based on the membrane selectivity of these conjugates, we have further demonstrated their applications in differentiating bacterial strains and potentially in pathogen detection. These lipid–DNA conjugates are promising tools to facilitate the possibly broad usage of DNA nanotechnology for bacterial membrane analysis, functionalization, and therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...