Click activated protodrugs against cancer increase the therapeutic potential of chemotherapy through local capture and activation†
Abstract
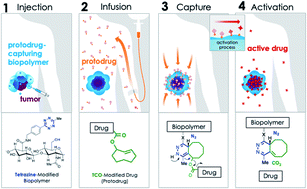
A desired goal of targeted cancer treatments is to achieve high tumor specificity with minimal side effects. Despite recent advances, this remains difficult to achieve in practice as most approaches rely on biomarkers or physiological differences between malignant and healthy tissue, and thus benefit only a subset of patients in need of treatment. To address this unmet need, we introduced a Click Activated Protodrugs Against Cancer (CAPAC) platform that enables targeted activation of drugs at a specific site in the body, i.e., a tumor. In contrast to antibodies (mAbs, ADCs) and other targeted approaches, the mechanism of action is based on in vivo click chemistry, and is thus independent of tumor biomarker expression or factors such as enzymatic activity, pH, or oxygen levels. The CAPAC platform consists of a tetrazine-modified sodium hyaluronate-based biopolymer injected at a tumor site, followed by one or more doses of a trans-cyclooctene (TCO)-modified cytotoxic protodrug with attenuated activity administered systemically. The protodrug is captured locally by the biopolymer through an inverse electron-demand Diels–Alder reaction between tetrazine and TCO, followed by conversion to the active drug directly at the tumor site, thereby overcoming the systemic limitations of conventional chemotherapy or the need for specific biomarkers of traditional targeted therapies. Here, TCO-modified protodrugs of four prominent cytotoxics (doxorubicin, paclitaxel, etoposide and gemcitabine) are used, highlighting the modularity of the CAPAC platform. In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity, solubility, stability and activation rendered the protodrug of doxorubicin, SQP33, as the most promising candidate for in vivo studies. In mice, the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of SQP33 in combination with locally injected tetrazine-modified biopolymer (SQL70) was determined to be 19.1-times the MTD of conventional doxorubicin. Pharmacokinetics studies in rats show that a single injection of SQL70 efficiently captures multiple SQP33 protodrug doses given cumulatively at 10.8-times the MTD of conventional doxorubicin with greatly reduced systemic toxicity. Finally, combined treatment with SQL70 and SQP33 (together called SQ3370) showed antitumor activity in a syngeneic tumor model in mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...