pH-controlled DNA- and RNA-templated assembly of short oligomers†
Abstract
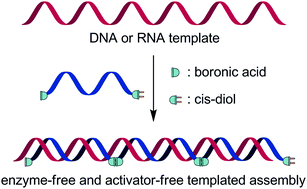
In the area of artificial genetics the development of non-enzymatic self-organization of synthetic building blocks is critical for both providing biopolymers with extended functions and understanding prebiotic processes. While reversibility is believed to have played a major role in early functional genetic materials, we previously reported an efficient DNA-templated ligation of suitably designed 5′-end boronic acid and 3′-end ribonucleosidic half-sequences. Here, we report the enzyme-free and activation-free DNA- and RNA-templated assembly of bifunctional hexamers. The reversible assembly was found to be regio- and sequence specific and the stabilities of the resulting duplexes were compared to their nicked counterparts. To go further with our understanding of this unprecedented process we also examined an auto-templated duplex self-assembly representing a key step toward the evolution of sequence-defined synthetic polymers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...