Damage of EPS and cell structures and improvement of high-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge by combined (Ca(OH)2 + multiple-transducer ultrasonic) pretreatment
Abstract
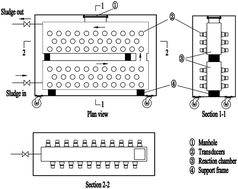
The effects of individual and combined full-scale Ca(OH)2 and ultrasonic pretreatment on high-solid sludge (total solids content = 8%) were examined in terms of soluble organics increase, damage of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) and cell structures, and subsequent anaerobic digestion. The maximum solubilization difference was obtained when combined pretreatment of 0.04 g g−1-TS lime and 225 kJ kg−1-TS ultrasound was used. The individual 0.04 g g−1 TS lime and low power ultrasonic pretreatment could only disintegrate the EPS partly, while the combined pretreatment damage not only EPS but also cells. Compared with the individual pretreatment, the combined pretreatment could result in a better performance of anaerobic digestion. When 0.04 g g−1-TS lime and 225 kJ kg−1-TS ultrasonic pretreatment was applied, the cumulative methane yield increased by 36.7% compared with that of individual lime pretreatment. These results proved that the multiple-transducer ultrasonic process could disintegrate high-solid sludge effectively when combined with Ca(OH)2, as well as enhance the methane yield.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...