Design and synthesis of uracil urea derivatives as potent and selective fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors†
Abstract
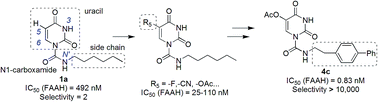
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is one of the key enzymes involved in the biological degradation of endocannabinoids, especially anandamide. Pharmacological blockage of FAAH restores the levels of endocannabinoids, providing therapeutic benefits in the management of inflammation, depression and multiple sclerosis. In this study, a series of uracil urea derivatives as FAAH inhibitors were designed and synthesized. Structural modifications at the C5 position and side chain of N-hexyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-1(2H)-carboxamide (1a) led to FAAH inhibitors with improved potency and selectivity. Structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies indicated that C5 electron-withdrawing substituents were preferred for optimal potency but not for selectivity, whereas replacement of the alkyl chain with phenylalkyl moieties or biphenyl groups significantly improved both inhibitory potency and selectivity towards FAAH. Two highly potent picomolar FAAH inhibitors (4c, IC50 = 0.3 ± 0.05 nM; 4d, IC50 = 0.8 ± 0.1 nM) were developed. Compound 4c inhibited FAAH in a rapid, selective, noncompetitive, and irreversible pattern. This study provides several highly potent and selective FAAH inhibitors and an optimized chemical scaffold for the development of FAAH inhibitors. We anticipate that these FAAH inhibitors will enable new possibilities in understanding FAAH functions and development of therapeutics for pain and inflammatory diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...