Influence of trehalose on human islet amyloid polypeptide fibrillation and aggregation
Abstract
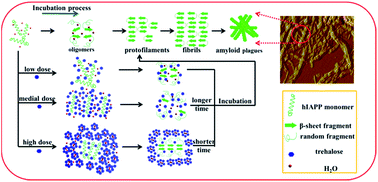
Abnormal denaturation and aggregation of human amylin or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) into amyloid fibrils has been implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetic mellitus. Trehalose, a super-hydrophilic molecule, has been shown to prevent denaturation of biomolecules when they are under environmental stress. In this work, we sought to investigate the effects of trehalose on the fibrillation and aggregation of human IAPP (hIAPP) by using circular dichroism spectrum, thioflavin-T fluorescence spectrum, dynamic light scattering, transmission electronic microscopy, atomic force microscopy and quartz crystal microbalance. We demonstrated that (1) the conformation of hIAPP changed from α-helix to β-sheet, followed by fibrillation and aggregation, (2) a low dose of trehalose (under 100 mM) inhibited or delayed the conformation transition of hIAPP and (3) a high dose (more than 500 mM) induced the conformation transition, and promoted the fibrillation and aggregation of hIAPP. These findings are in agreement with the hypothesis of the water replacement and volume exclusion effect on the proteins. The lower concentration of trehalose could replace the water molecules surrounding the hIAPP, and interact with proteins through hydrogen bonding, leading to a reduction in the protein interaction itself, and therefore inhibiting or delaying the protein fibrillation and aggregation. In contrast, the higher concentration of trehalose might interact with itself to form macromolecular clusters, acting as a crowding agent, leading to the hIAPP molecules being excluded by the trehalose clusters and interacting between each other, and therefore promoting the hIAPP fibrillation and aggregation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...