Surface functionalization-induced enhancement in surface properties and biocompatibility of polyaniline nanofibers†
Abstract
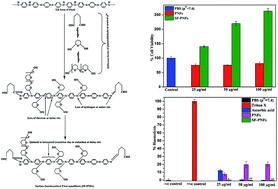
Nanofibers of polyaniline (PAni) have been synthesized by a dilute polymerization method and functionalized by 1% glutaraldehyde solution in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) (pH = 7.4) and in thin films to introduce a polar chemical group in order to develop a novel bioactive platform for tissue engineering applications. TEM estimates the nanofibers to have an average diameter of 35.66 nm. FESEM images confirm the presence of interconnected nanofibrous structures of PAni powder and the highly entangled morphology of the films. Thermogravimetric analysis indicates enhanced thermal stability of polyaniline nanofibers (PNFs) after functionalization. UV-visible absorption and photoluminescence studies demonstrate that PNFs are in emeraldine base (EB) form before and after functionalization. FTIR and NMR spectroscopic studies reveal successful incorporation of polar hydroxyl (–OH) and aldehyde (–CHO) groups into the PNFs. Contact angle measurements demonstrate an increase in wettability of PAni films after surface functionalization as the contact angle decreases from 76.2° to 52.1°. Surface energy calculations using OWRK (Owens, Wendt, Rabel and Kaelble) and AB (acid–base) methods show an increase in energy and polarity of the surface, endowing it with biocompatibility. Membrane stability tests reveal less haemolysis activity by surface-functionalized polyaniline nanofibers (SF-PNFs). MTT assay of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) shows a significant increase in cell viability after surface functionalization of PNFs. The non-cytotoxic effects of SF-PNFs make them a biocompatible scaffold for biomedical applications such as tissue engineering and drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...