A macrocyclic oligoelectrolyte as a facial platform for absorbing hyaluronic acid oligomers for targeted cancer cellular imaging
Abstract
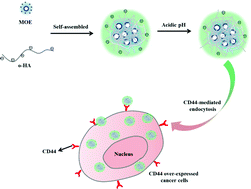
A novel water-soluble macrocyclic oligoelectrolyte (MOE) was designed and synthesized by a simple Friedel–Crafts reaction as a facial platform for fabricating biological nanoparticles. The produced MOE with a unique three-dimension (3D) rigid structure consisted of a triphenylamine-based cyclic core and three oligofluorene arms, which protruded from the ring plane on both sides. The specific structure rendered MOE with good photoluminescence (PL) stabilities, low aggregation tendencies and excellent water-soluble properties in the form of well-defined smart organic dots (sub-10 nm) in aqueous solution. Using these organic dots as a template and OHAs, a biocompatible and linear oligosaccharide made straightforward contact with CD44 (a principal cell surface receptor for HA). As a stabilizer and biomarker, functional nanoparticles (MHNs-0.4) were fabricated via electronic interaction induced self-assembly in aqueous solution. The final confirmed MHNs-0.4 with suitable size (around 80 nm), good stability and fluorescent properties were found to be outstanding materials for the specific labelling of CD44-overexpressed human lung cancer cells (A549). The highlight of the study is that we provided a powerful and reliable platform, MOE-dots, for adsorbing various negatively charged molecules and broadening potential biological applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...