Synthesis of electroconductive hydrogel films by an electro-controlled click reaction and their application to drug delivery systems†
Abstract
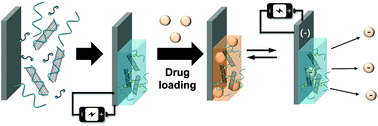
Electroconductive hydrogels are composed of 3-dimensionally structured hydrogels and conducting molecules with electrical, optical, and reversible redox properties. These hybrid materials can be utilized as electrically-stimulated biomaterials in implantable biosensors or drug delivery systems. In this study, carbon nanotube-incorporated polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-based hydrogels were synthesized by an electro-click reaction, which was controlled by an electrochemically generated Cu(I) catalyst. When the reduction potential of Cu(II) ions was applied, PVA-based hydrogels were deposited onto indium-tin-oxide-coated glass electrodes via Cu(I)-catalysed alkyne–azide cycloaddition (click reaction). When the hydrogels contained carbon nanotubes, thicker films were deposited because the embedded carbon nanotubes provided a larger electrochemical active area. In addition, the carbon nanotubes improved the electrical conductivity of the hydrogel systems. We investigated the electro-stimulated drug release behaviour with electro-click conductive hydrogels using tetracycline as a model drug.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...