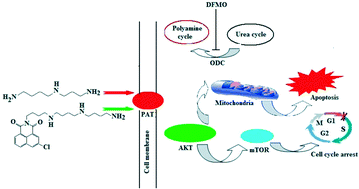
Though several naphthalimide derivatives have exhibited antitumor activity in clinical trials, some issues such as toxicity prompted further structural modifications on the naphthalimide backbone. A series of naphthalimides conjugated with polyamines were synthesized to harness the polyamine transporter (PAT) for drug delivery, which was beneficial for the tumor cell selectivity. Bioevaluation in human hepatoma HepG2 cells treated with α-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) or spermidine (Spd), human hepatoma Bel-7402 and normal QSG-7701 hepatocyte confirmed the PAT recognition and cell selectivity. In addition, the novel naphthalimide polyamine conjugate kills cellsviaapoptosis, and the Akt/mTOR signal pathway was first identified as the upstream cellular target through the apoptotic mechanism research. The presence of DFMO or Spd only either elevated or attenuated the cell apoptosis, but did not change the signal pathway. Collectively, the proper polyamine recognition element (i.e., homospermidine) mediated effective drug delivery via the PAT, and helped the proper cytotoxic goods (i.e., diverse naphthalimides) exert antitumor properties.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...