Si microstructures laminated with a nanolayer of TiO2 as long-term stable and effective photocathodes in PEC devices
Abstract
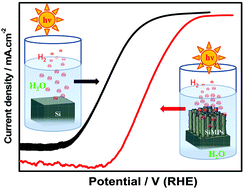
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is one of the most emerging fields for green energy generation and storage. Here we show a study of microstructured Si covered by a TiO2 nano-layer. The microstructures are prepared by galvanostatic selective etching of Si. The TiO2 nano-layer was deposited by atomic layer deposition (ALD) to protect the microstructured photocathode against corrosion. The obtained microstructured photocathode showed a shift in the onset potential of 400 mV towards the anodic direction compared to bare Si. The Si microstructures laminated with a nano-layer of TiO2 show stability over 60 hours of measurement.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...