Silicon nanoparticles coated with nanoporous carbon as a promising anode material for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
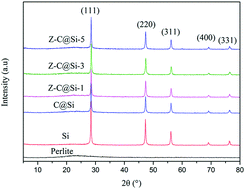
As a promising anode candidate, silicon (Si) nanoparticles have been widely studied for use in lithium ion batteries. However, Si nanoparticles suffer from the disadvantage of volume expansion during lithiation/delithiation, which leads to irreversible capacity decrease. In this work, perlite is utilized to prepare Si nanoparticles via magnesiothermic reduction. To alleviate the volume expansion of Si nanoparticles, a nanoporous carbon is prepared to coat Si nanoparticles using chitosan (C) as the carbon source and zinc chloride (Z) as the pore former. TEM micrographs show that the porous carbon with mesoporous size has formed and coated the surface of Si nanoparticles. The prepared carbon coated Si sample (Z-C@Si-5 contains 5 times the mass ratio of Z to C) exhibits suitable pore volume (0.576 cm3 g−1) and pore size (4–6 nm), as well as excellent specific surface area (418.315 m2 g−1) The obtained Z-C@Si-5 also shows promising electrochemical performance with a reversible capacity of 2064.11 mA h g−1 at 0.2C and 847.32 mA h g−1 at 4C, as well as a high capacity retention. The promising electrochemical performance originated from the nanoporous carbon coating, which not only effectively alleviated the volume expansion problem of Si, but also provided a rapid transport channel of lithium ions through its nanoporous structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...