pH and molecular weight dependence of auric acid reduction by polyethylenimine and the gene transfection efficiency of cationic gold nanoparticles thereof†
Abstract
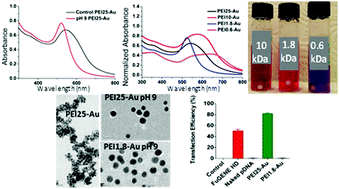
Small, cationic gold nanoparticles (GNP) are produced by the direct reduction of auric acid in a non-reducing solvent, water, with branched polyethylenimine (bPEI) in a broad pH range (3.0–9.0). Basic pH, which is studied for the first time, emerged as a favorable condition to achieve good reducing power and surface passivation simultaneously, providing smaller particles (hydrodynamic size ca. 6 nm) with enhanced long-term stability and a sharper surface plasmon peak (SPP). This synthetic method produces colloidal GNPs with bPEI in a broad molecular weight range (0.6, 1.8, 10 and 25 kDa). The molecular weight did not influence the crystal size much but did affect the hydrodynamic size and the stability. 0.6 kDa bPEI provides the largest GNPs (ca. 100 nm aggregates) which lack long term stability. 1.8 kDa bPEI provides small particles (hydrodynamic size ca. 7 nm) with the sharpest SPP. The GNPs prepared with 25 and 1.8 kDa bPEI show no significant cytotoxicity in HEK 293T cells and PEI25–Au transfects green fluorescent protein (GFP) into HEK 293T cells more efficiently (82%) than FuGENE® (50%). This simple one pot synthesis of cationic GNPs in water is a valuable, simple alternative for the generation of new cationic GNPs in water with even low molecular weight PEI.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...