Dinuclear first-row transition metal–(C8Me6)2 complexes: metal–metal and metal–ligand bonds determined by the d electron configuration of the metal atom†
Abstract
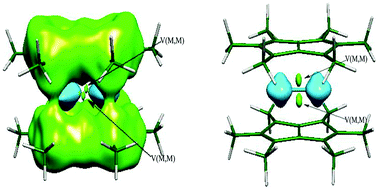
The metal–metal and metal–ligand bonds in the bimetallic sandwich compounds Pn*2M2 (Pn* = C8Me6; M = Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu) have been investigated using the atoms in molecules (AIM) theory, electron location function (ELF), and electron decomposition analysis (EDA). The calculated results indicate that the strength of the metal–metal (M–M) bond and the coordination mode of the Pn* ligands to a pair of metal atoms depend on the d electron configuration of the transition metal. The more unpaired d electrons, the higher the coordination number of the metal to the ligands, which increases from η1 to η5. The stronger the metal–ligand interaction, the weaker the contribution of the electrostatic interaction to the metal–ligand interaction. The strength of the M–M bonds increases in the sequence M = Sc < Ti < V, and decreases in the sequence V > Cr > Mn > Fe > Co > Ni > Cu. The V–V bond is the strongest of the studied dinuclear first-row transition metal–(C8Me6)2 complexes. The studied M–M bonds are metallic bonds and have a partially covalent character, except for Sc–Sc which is a covalent bond and Cu–Cu which is an electrostatic interaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...