Characterization of selective binding of biologically relevant inorganic ions with the proline zwitterion by 3D-RISM theory
Abstract
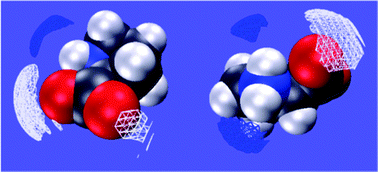
Selective binding between the charged groups of the proline zwitterion (Pro-ZW) and several biologically relevant mono- and divalent inorganic ions (Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl−) was studied over a wide range of electrolyte concentrations using integral equation theory in the three-Dimensional Reference Interaction Site Model (3D-RISM) approach. These model samples mimic ion pairing between charged functional groups at protein surfaces and physiologically relevant ions. The effects of salt concentration and chemical nature of the inorganic ion on the stability of the formed ion–molecular associates are analyzed. Additionally, the possible mechanism of ion binding and the structure of the formed aggregates are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...