Fusion of genomic, proteomic and phenotypic data: the case of potyviruses†
Abstract
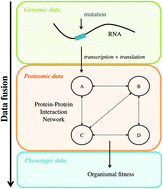
Data fusion has been widely applied to analyse different sources of information, combining all of them in a single multivariate model. This methodology is mandatory when different omic data sets must be integrated to fully understand an organism using a systems biology approach. Here, a data fusion procedure is presented to combine genomic, proteomic and phenotypic data sets gathered for Tobacco etch virus (TEV). The genomic data correspond to random mutations inserted in most viral genes. The proteomic data represent both the effect of these mutations on the encoded proteins and the perturbation induced by the mutated proteins to their neighbours in the protein–protein interaction network (PPIN). Finally, the phenotypic trait evaluated for each mutant virus is replicative fitness. To analyse these three sources of information a Partial Least Squares (PLS) regression model is fitted in order to extract the latent variables from data that explain (and relate) the significant variables to the fitness of TEV. The final output of this methodology is a set of functional modules of the PPIN relating topology and mutations with fitness. Throughout the re-analysis of these diverse TEV data, we generated valuable information on the mechanism of action of certain mutations and how they translate into organismal fitness. Results show that the effect of some mutations goes beyond the protein they directly affect and spreads on the PPIN to neighbour proteins, thus defining functional modules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...