Stretchable impedance sensor for mammalian cell proliferation measurements
Abstract
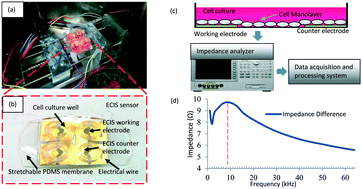
This paper presents the fabrication and testing of a novel stretchable electric cell–substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) lab on a chip device. This is the first time that ECIS electrodes were fabricated on a stretchable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrate and ECIS measurements were performed on mammalian cells exposed to cyclic strain. The stretchable ECIS biosensors simulate in vitro the dynamic environment of organisms, such as pulsation, bending and stretching, which enables investigations on cell behavior that undergoes mechanical stimuli in biological tissue. Usually cell-based assays used in cell mechanobiology rely on endpoint cell tests, which provide a limited view on dynamic cellular mechanisms. The ECIS technique is a label-free, real-time and noninvasive method to monitor the cellular response to mechanical stimuli. Bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) have been used in this research because the BAECs are exposed in vivo to cyclic physiologic elongation produced by blood circulation in the arteries. These innovative stretchable ECIS biosensors were used to analyze the proliferation of BAECs under different cyclic mechanical stimulations. The results of fluorescence based cell proliferation assays confirmed that the stretchable ECIS sensors were able to analyze in real-time the BAEC proliferation. The novel stretchable ECIS sensor has the ability to analyse cell proliferation, determine the cell number and density, and apply mechanical stimulation at the same time.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...