A contact active bactericidal stainless steel via a sustainable process utilizing electrodeposition and covalent attachment in water†
Abstract
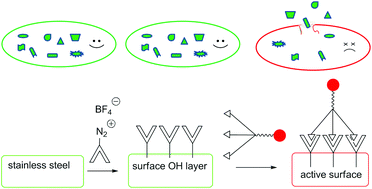
A contact active bactericidal stainless steel was synthesized in water utilizing phenol electrodeposition, followed by covalent attachment of quaternary ammonium salts. The approach minimizes the amount of the antimicrobial agent and avoids its release into the environment. Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria were inactivated upon contact with the modified surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...