Chemo-enzymatic synthesis route to poly(glucosyl-acrylates) using glucosidase from almonds†
Abstract
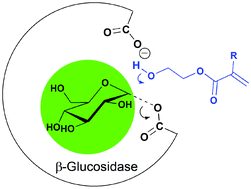
Novel types of glucosyl-acrylate monomers are obtained by β-glucosidase from almond catalyzed glycosidation reaction. The saccharide-acrylate monomers were synthesized by reaction of D-glucose with hydroxyl functional acrylates: 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (2-HEA), 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (2-HEMA) and 4-hydroxybutyl acrylate (4-HBA). The reaction products could be identified as 2-(β-glucosyloxy)-ethyl acrylate, 2-(β-glucosyloxy)-ethyl methacrylate and 4-(β-glucosyloxy)-ethyl acrylate respectively. The synthesis yield was optimized by variation of the 2-HEA–water ratio, the presence of water-miscible co-solvents and the reaction time. The optimal reaction mixture was found to contain 13 vol% water, 80 vol% 2-HEA and 7 vol%; 1.4-dioxane. The maximal yield under these conditions was 50 wt% based on D-glucose after 24 hours of reaction. The enzymatically synthesized glucosyl-acrylates were successfully polymerized by free radical polymerization in DMF and water. The glycosidic linkage of the glycosyl-acrylate monomers was retained during the polymerization process. The enzymatically synthesized glucosyl-acrylates could be successfully copolymerized with vinyl monomers 2-HEA, 2-HEMA, methacryl amide and N-vinyl imidazole.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...