Homo- and heteropolynuclear Ni2+ and Cu2+ complexes of polytopic ligands, consisting of a tren unit substituted with three 12-membered tetraazamacrocycles†
Abstract
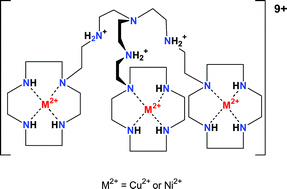
Two new polytopic ligands L1 and L2 have been synthesized. They consist of a central tren unit to which three 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane rings are attached via an ethylene and a trimethylene bridge, respectively. The complexation properties of L1 and L2 towards Cu2+ and Ni2+ were studied by potentiometric pH titration, UV-Vis, EPR spectroscopy and kinetic techniques. As a comparison, the Cu2+ and Ni2+ complexes with L3 (1-(N-methyl-2-aminoethyl-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane)) were also investigated. The crystal structures of [CuL3H(H2O)](ClO4)3 and [NiL3Cl](ClO4) were solved and show that the side chain in its protonated form is not involved in coordination, whereas deprotonated it binds to the metal ion. The thermodynamically stable 3 : 1 complexes of L1 or L2 have a metal ion in the three macrocyclic units. However, when three equivalents of Cu2+ are added to L1 or L2 the metal ion first binds to the tren unit and only then to the macrocycles. The kinetics of the different steps of complexation have been studied and a mechanism is proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...