Surface charge-dependent hydrodynamic properties of an electroosmotic slip flow
Abstract
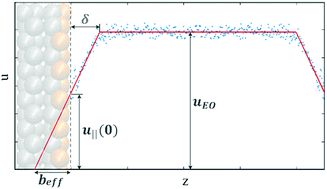
The electroosmosis effects at the interface of an aqueous NaCl solution and a charged silicon surface are studied using a molecular dynamics (MD) method. Considering a plug-like electroosmotic flow, we identified a thin interfacial layer in the immediate vicinity of the charged surface, where the flow velocity experiences almost linear spatial variations. The thickness of this interfacial layer is found to be linearly dependent on the surface charge density, with a negative slope which slightly depends on the surface hydrophobicity while being independent of the salt concentration, electric field strength, and orientation of the surface lattice. It is also found that upon increasing the surface charge density, the effective slip length first increases up to a maximum amount and then follows an almost linear reduction. We found that increasing the salt concentration drastically reduces the surface charge at which the effective slip length reaches its maximum amount. For highly concentrated solutions, therefore, the effective slip length could be assumed to change linearly in the whole range of the surface charge density, with a slope which is proportional to the square root of the electric field strength 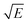 divided by the depth of the potential well assigned to the surface atoms εwall. Also, in a wide range of the surface charge density, the slip velocity is found to be a constant fraction of the electroosmotic velocity, which could be measured experimentally. Finally, by comparing the electroosmotic velocities calculated from the Stokes equation (considering both the slip and no-slip boundary conditions) with our MD results, we found that the no-slip boundary condition, which is normally used in analytical calculations, leads to a very inaccurate result for the studied system.
divided by the depth of the potential well assigned to the surface atoms εwall. Also, in a wide range of the surface charge density, the slip velocity is found to be a constant fraction of the electroosmotic velocity, which could be measured experimentally. Finally, by comparing the electroosmotic velocities calculated from the Stokes equation (considering both the slip and no-slip boundary conditions) with our MD results, we found that the no-slip boundary condition, which is normally used in analytical calculations, leads to a very inaccurate result for the studied system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...