Suppression of near band edge emission in specially engineered ZnO twin nanorods
Abstract
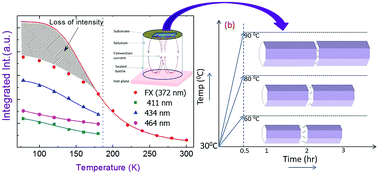
We report the synthesis of a unique zinc oxide nanorod structure in which an amorphous ZnO layer is sandwiched between two identical crystalline segments of ZnO. A simple hydrothermal reaction method was used for this purpose, which allowed us to tune the amorphous and crystalline sections of the nanorods via reaction temperature. A systematic study of the morphology and dimensions of the nanorods grown under various conditions was performed using a combination of scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) clearly showed an amorphous separation between the two crystalline segments. UV-vis absorption spectroscopy of the twin nanorods (TNRs) showed a redshift in the optical band gap as a function of the growth duration, indicating slightly stressed growth of the crystalline segments. For a longer growth duration, as the amorphous gap starts to get bridged by crystalline growth, redshift in optical band gap becomes constant. This confirms a true mechanical gap between the two crystalline segments of the nanorods. Temperature dependent photoluminescence (PL) spectra of the TNRs showed a variation in free exciton (FX) emission energy, which fitted very well to a model incorporating lattice dilation in addition to the standard electron–phonon interactions. At low temperatures (below ∼180 K) we observed the appearance of visible emission peaks due to localization of defect levels. A loss in the near band edge emission intensity was observed at low temperatures, commensurate with the appearance of defect emission in the visible range.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...