Mechanical and molecular basis for the symmetrical division of the fission yeast nuclear envelope
Abstract
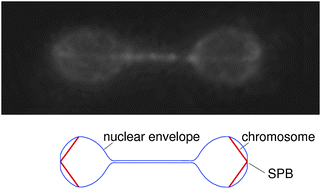
In fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, the nuclear envelope remains intact throughout mitosis and undergoes a series of symmetrical morphological changes when the spindle pole bodies (SPBs), embedded in the nuclear envelope, are pushed apart by elongating spindle microtubules. These symmetrical membrane shape transformations do not correspond to the shape behavior of an analogous system based on lipid vesicles. Here we report that the symmetry of the dividing fission yeast nucleus is ensured by SPB–chromosome attachments, as loss of kinetochore clustering in the vicinity of SPBs results in the formation of abnormal asymmetric shapes with long membrane tethers. We integrated these findings in a biophysical model, which explains the symmetry of the nuclear shapes on the basis of forces exerted by chromosomes clustered at SPBs on the extending nuclear envelope. Based on this analysis we conclude that the fission yeast nuclear envelope exhibits the same mechanical properties as simple lipid vesicles, but interactions with other cellular components, such as chromosomes, influence the nuclear shape during mitosis, allowing the formation of otherwise energetically unfavorable symmetrical dumbbell structures upon spindle elongation. The model allows us to explain the appearance of abnormal asymmetric shapes in fission yeast mutants with mis-segregated chromosomes as well as with altered nuclear membrane composition.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical compartmentalisation by membranes: from biological mechanism to biomimetic applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...