Design of isolated iron species for Fenton reactions: lyophilization beats calcination treatment†
Abstract
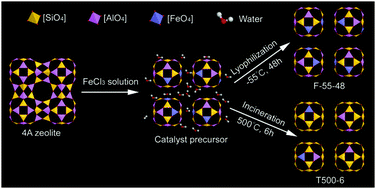
Lyophilization is used to prepare a Fenton catalyst containing a predominant amount of isolated Fe3+ species with an 8.90% iron content. This catalyst shows a higher catalytic rate and H2O2 utilization efficiency but lower iron leaching in phenol degradation, compared with the calcination sample.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...