Evidence for hydrophobic catalysis of DNA strand exchange†
Abstract
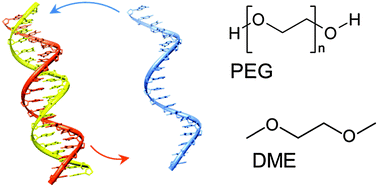
The catalytic role of hydrophobic co-solutes in DNA strand exchange is demonstrated by FRET kinetics. Two mechanisms that contribute to this are base stacking destabilisation and nucleation-promoted DNA strand invasion. We propose that hydrophobic catalysis is involved in the strand-exchange activity of recombination enzymes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...