Pressure-driven spreadable deferoxamine-laden hydrogels for vascularized skin flaps†
Abstract
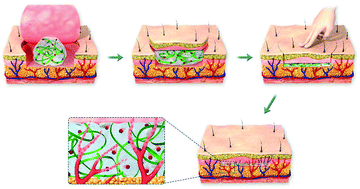
The development of hydrogels that support vascularization to improve the survival of skin flaps, yet establishing homogeneous angiogenic niches without compromising the ease of use in surgical settings remains a challenge. Here, pressure-driven spreadable hydrogels were developed utilizing beta-sheet rich silk nanofiber materials. These silk nanofiber-based hydrogels exhibited excellent spreading under mild pressure to form a thin coating to cover all the regions of the skin flaps. Deferoxamine (DFO) was loaded onto the silk nanofibers to support vascularization and these DFO-laden hydrogels were implanted under skin flaps in rats to fill the interface between the wound bed and the flap using the applied pressure. The thickness of the spread hydrogels was below 200 μm, minimizing the physical barrier effects from the hydrogels. The distribution of the hydrogels provided homogeneous angiogenic stimulation, accelerating rapid blood vessel network formation and significantly improving the survival of the skin flaps. The hydrogels also modulated the immune reactions, further facilitating the regeneration of the skin flaps. Considering the homogeneous distribution at the wound sites, improved vascularization, reduced barrier effects and low inflammation, these hydrogels appear to be promising candidates for use in tissue repair where a high blood supply is in demand. The pressure-driven spreading properties should simplify the use of the hydrogels in surgical settings to facilitate clinical translation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...