The role of lithium in the osteogenic bioactivity of clay nanoparticles†
Abstract
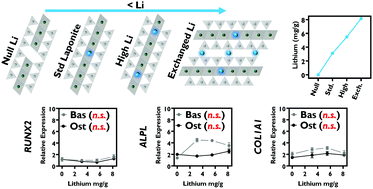
LAPONITE® clay nanoparticles are known to exert osteogenic effects on human bone marrow stromal cells (HBMSCs), most characteristically, an upregulation in alkaline phosphatase activity and increased calcium deposition. The specific properties of LAPONITE® that impart its bioactivity are not known. In this study the role of lithium, a LAPONITE® degradation product, was investigated through the use of lithium salts and lithium modified LAPONITE® formulations. In contrast to intact particles, lithium ions applied at concentrations equivalent to that present in LAPONITE®, failed to induce any significant increase in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity. Furthermore, no significant differences were observed in ALP activity with modified clay structures and the positive effect on osteogenic gene expression did not correlate with the lithium content of modified clays. These results suggest that other properties of LAPONITE® nanoparticles, and not their lithium content, are responsible for their bioactivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...