Hydrophilic and degradable polyesters based on l-aspartic acid with antibacterial properties for potential application in hernia repair
Abstract
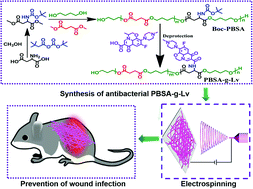
A polyester hernia patch has received extensive attention in mesh hernia repair. However, it is still a challenge to develop polyester-based implants with inherent antibacterial properties due to the lack of active functional groups. In this study, poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene aspartate) (PBSA) was constructed by introducing aspartic acid on a polybutylene succinate (PBS) polyester chain (PBSA). Antimicrobial treatment was conducted by grafting levofloxacin (Lv) on the surface of a PBSA polymer (PBSA-g-Lv). In vitro antibacterial test results showed that PBSA-g-Lv had sufficient local antimicrobiotic effects against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli and no side effect on L929 cells was observed. Furthermore, almost no change was observed in the thermodynamic properties of PBS and PBSA; in vivo tests demonstrated that this contact-active antibacterial PBSA-g-Lv nanofiber is a promising material to fulfill the dual functions of promoting tissue regeneration and preventing bacterial infection. The presented data confirmed that an antibiotic surface modification of PBSA polyesters was expected to be used as hernia repair materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...