CO2-effervescence assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction based on a magnetic layered double hydroxide modified with polyaniline and a surfactant for efficient pre-concentration of heavy metals in cosmetic samples
Abstract
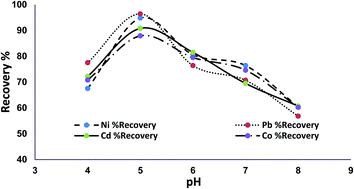
In this paper, a CO2-effervescence assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction procedure (CO2-EA-DμSPE) using a magnetic layered double hydroxide modified with polyaniline and a surfactant (Zn–Al–LDH–PA–DBSNa–Fe3O4) was applied for the pre-concentration of heavy metals (Ni2+, Pb2+, Co2+, and Cd2+). The final analysis of the analytes was carried out by atomic absorption spectroscopy. XRD, FTIR, and SEM studies were used for the characterization of the synthesized nanoadsorbent. For the maximum extraction efficiency, effective factors (including pH, nanoadsorbent dosage, and volume of the eluent) were investigated using the central composite design (CCD) method. Under the optimum conditions, the preconcentration factor was more than 20. The linear ranges for Ni2+, Pb2+, Co2+, and Cd2+ were obtained as (5–550), (7–750), (5–500), and (3–100) ng mL−1, respectively. The proposed method provided low detection limits (1.4, 2.1, 1.5, and 0.9 ng mL−1 for Ni2+, Pb2+, Co2+, and Cd2+, respectively) and suitable repeatability (relative standard deviation values (RSDs) below 6.1%, n = 6). Finally, the current method was successfully used for the extraction of heavy metals from cosmetic samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...