Study on the treatment effect of Polygonum cuspidatum for hyperuricemia in rats using the UPLC-ESI-QTOF/MS metabolomics approach†
Abstract
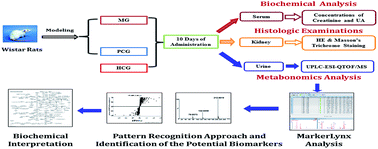
A urinary metabolomics study based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization quadruple time-of-flight/mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-QTOF/MS) coupled with a pattern recognition approach was conducted to study the mechanism of Polygonum cuspidatum, a traditional Chinese medicine, in treating hyperuricemic rats. Moreover, serum samples for biochemical measurements and kidney samples for histopathology were collected and measured. The results showed that a clear separation among healthy control rats, hyperuricemic rats and Polygonum cuspidatum-treated rats was achieved by using pattern recognition approaches including principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA). It revealed that Polygonum cuspidatum could prevent the pathological process of hyperuricemia by regulating eighteen potential biomarkers associated with purine metabolism, tryptophan metabolism, tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, phenylalanine metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, valine metabolism and tyrosine metabolism. The biochemical assay and histopathological assay confirmed that Polygonum cuspidatum could significantly reduce uric acid and showed a protective effect on kidneys of hyperuricemic rats.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...