Determination of aluminum and silicon in bovine liver by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after dissolution with tetramethylammonium hydroxide
Abstract
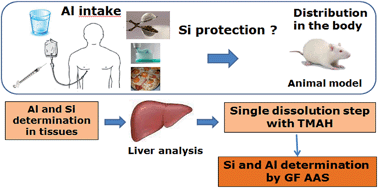
Studies suggest that silicic acid or silica can reduce the oral absorption and increase the excretion of aluminum thus protecting the organism against the adverse effects induced by this metal. Therefore, the simultaneous or concomitant determination of Al and Si in biological samples is of significance. In this study a method for sample treatment and the determination of both Al and Si by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS) in animal tissue was developed. Sample dissolution with tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) proved to be suitable for the determination of both elements. Because Si enhances the Al signal during atomization, this element acted as a chemical modifier for the determination of Al. For the determination of Si, palladium nitrate was the most suitable modifier. The use of Zr as a permanent modifier minimized the tube degradation caused by TMAH. The limits of detection were 5.8 μg L−1 for Al and 29.0 μg L−1 for Si, and the recoveries in spiked samples were between 97 and 112%. The method was validated against bovine liver standard reference materials (SRM 1577b and 1577c), and the obtained concentrations agreed with the certified values.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...