Nuclear relaxation in agar gel in the presence of highly concentrated PEG coated magnetic nanoparticles at low magnetic fields. Application of temperature dependent
 weighting for MRI thermometry
weighting for MRI thermometry
Abstract
Magnetic nanoparticles are used to map the temperature of the human body using MRI because their presence influences proton relaxation times. Especially at low fields, proton relaxation times exhibit strong temperature dependence, enabling precise determination of local temperature within a body with high resolution. As an illustration, we report temperature-dependent NMR and MRI investigations of agar gel with embedded Mn0.48Zn0.46Fe2.06O4 ferrite nanoparticles, evaluated as potential temperature–sensitive exogenous MRI contrast agents at low magnetic fields for noninvasive MRI thermometry. The nanoparticles consisted of an 8.5 nm magnetic core that were coated with a PEG shell, yielding a hydrodynamic diameter of 20 nm. Spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) profiles were obtained using a Fast Field Cycling NMR relaxometer. The 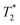 – weighted gradient echo MR images at 0.2 T were obtained in a temperature range of 23 °C to 50.5 °C, encompassing physiologically relevant values. Simulations of MR image intensity at 0.2 T, based on experimental T1 and
– weighted gradient echo MR images at 0.2 T were obtained in a temperature range of 23 °C to 50.5 °C, encompassing physiologically relevant values. Simulations of MR image intensity at 0.2 T, based on experimental T1 and 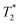 values, were carried out and compared with the corresponding temperature-dependent experimental images. Analysis of our measurements indicated that the temperature was determined with 2 °C accuracy.
values, were carried out and compared with the corresponding temperature-dependent experimental images. Analysis of our measurements indicated that the temperature was determined with 2 °C accuracy.




 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
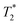 weighting for MRI thermometry
weighting for MRI thermometry