Selective α-oxidation of amides via visible-light-driven iron catalysis†
Abstract
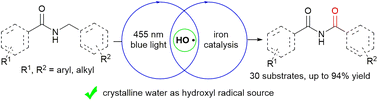
Hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) as one of the highly reactive species can react unselectively with a wide range of chemicals. The ˙OH radicals are typically generated under harsh conditions. Herein, we report hydroxyl radical-induced selective N-α C(sp3)–H bond oxidation of amides under greener and mild conditions via an Fe(NO3)3·9H2O catalyst inner sphere pathway upon irradiation with a 30 W blue LED light strip (λ = 455 nm) using NaBrO3 as the oxidant. This protocol exhibited high chemoselectivity and excellent functional group tolerance. A preliminary mechanism investigation demonstrated that the iron catalyst afforded hydroxyl radicals via the visible-light-induced homolysis (VLIH) of iron complexes followed by a hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) process to realize this transformation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...