Fabrication of a tough, long-lasting adhesive hydrogel patch via the synergy of interfacial entanglement and adhesion group densification†
Abstract
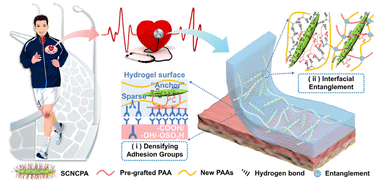
Adhesive hydrogels (AHs) are considered ideal materials for flexible sensors. However, the lack of effective energy dissipation networks and sparse surface polar groups in AHs lead to poor mechanical properties and interfacial adhesion, which limit their practical application. Herein, a tough, long-lasting adhesive and highly conductive nanocomposite hydrogel (PACPH) was fabricated via the synergy of interfacial entanglement and adhesion group densification. PACPH was obtained by the in situ polymerization of highly carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals (SCNCPA, surface pre-grafted polyacrylic acid chains, C–COOH = 11.5 mmol g−1) with the acrylic acid precursor. The unique tacticity of SCNCPA provides strong interface entanglement and multiple hydrogen bonds with the PACPH network, which further increases the energy dissipated during SCNCPA displacements, and enhances the mechanical properties of PACPH (tensile strength = 1.45 MPa, modulus = 332 kPa, and fracture toughness = 13.2 MJ m−3). Meanwhile, SCNCPA increases the density of surface polar groups in PAPCH and also acts as an anchor point to improve the adhesion strength (>2–3 times) of PACPH on various substrates. The combination of excellent mechanical, adhesive, and conductive properties of the PAPCH-integrated patches enables long-term monitoring of human daily activities and electrocardiogram (ECG) signals, verifying that PAPCH is a promising material platform for the further development of flexible sensors and other health management devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoscale 2024 Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...