Localized surface plasmon resonance shift of biosynthesized and functionalized quasi-spherical gold nanoparticle systems†
Abstract
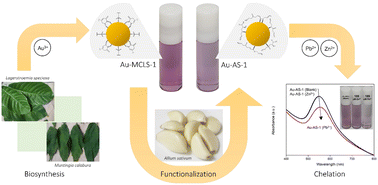
Rapid and more environment-friendly means of gold nanoparticle synthesis is necessary in many applications, as in ion detection. Leaf extracts have become effective and economical reducing agents for gold nanoparticle formation, however, effects of extract combinations have not been thoroughly investigated. With the exploitation of combined extract effects, gold nanoparticles were synthesized then functionalized and investigated to produce selected nanoparticle systems which are capable of detecting aqueous lead(II) ions with minimum detection limits of 10–11 ppm. The measured localized surface plasmon resonance absorption peaks of the gold nanoparticles were 541–800 nm for the synthesis and 549 nm for the functionalization. The diameters of different gold nanoparticle systems were 17–37 nm. These were mostly quasi-spherical in morphology with some rod-, triangular-, and hexagonal plate-like particles. The biosynthesis used polyphenols and acids present in the extracts in the reduction of gold ions into gold nanoparticles, and in the nanoparticle capping and stabilization. Functionalization replaced the capping compounds with alliin, S-allylcysteine, allicin, and ajoene. Gold nanoparticle stability in aqueous systems was verified for two weeks up to five months. The investigations concluded the practicability of the gold nanoparticles in lead(II) ion detection with selectivity initially verified for other divalent cations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...