A high-performance PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerator fabricated using surface-modified carbon nanotubes via pulsed laser ablation†
Abstract
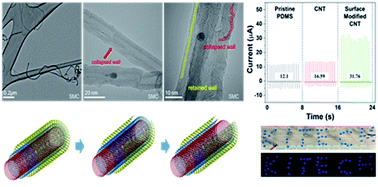
Poly-(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) has been used as a negative friction layer in triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) owing to its high electronegativity and flexibility. With the advantage of PDMS, the design of various materials to further enhance the energy output of a PDMS-based TENG system have been suggested for practical applications. Herein, we report a high-efficiency PDMS-based TENG wherein surface-modified carbon nanotubes (SMCs), fabricated by one-step pulsed laser ablation, were used as a PDMS additive. SMCs possess oxygen-rich functional groups on the surface that enhance their permittivity and dispersibility in PDMS. Consequently, improvements in the triboelectric performance and capacitance of an SMC-PDMS-based TENG device (SMC-PDMS) were observed, owing to the synergistic effects of the enhanced permittivity and dispersibility of SMCs. Compared to a pristine PDMS-based TENG, SMC-PDMS containing 0.05 wt% SMCs showed an output voltage of 382.12 V and a current of 29.44 μA, which correspond to 170% and 243% enhancements, respectively. In addition, a facile radio frequency plasma treatment was performed to further improve the performance of SMC-PDMS, resulting in an output voltage of 414.63 V, a current of 40.03 μA, and a power density of 7.69 W m−2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...