Bismuth nanoparticles embedded in a carbon skeleton as an anode for high power density potassium-ion batteries†
Abstract
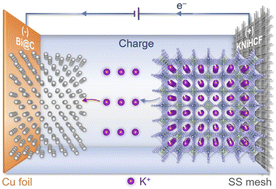
Bismuth is a promising anode for potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) due to its suitable redox potential, large theoretical capacity, and superior electronic conductivity. Herein, we report a Bi@C (Bi nanoparticles uniformly embedded in a carbon skeleton) composite anode which delivers a superior rate performance of 244.3 mA h g−1 at 10.0 A g−1 and a reversible capacity of 255.6 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles in an optimized ether-based electrolyte. The outstanding electrochemical performance results from its robust structural design with fast reaction kinetics, which are confirmed by both experimental characterization studies and first-principles calculations. The reversible potassium storage mechanism of the Bi@C composite was also investigated by in situ X-ray diffraction. In addition, the full PIB cell assembled with a Bi@C composite anode and nickel-based Prussian blue analogue cathode exhibits high discharge voltage (3.18 V), remarkable power density (>10 kW kg−1), and an excellent capacity retention of 87.8% after 100 cycles. The results demonstrate that the PIBs with Bi anodes are promising candidates for power-type energy storage devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...