Universal encoding of next generation DNA-encoded chemical libraries†
Abstract
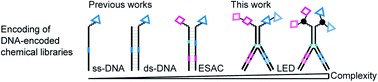
DNA-encoded chemical libraries (DELs) are useful tools for the discovery of small molecule ligands to protein targets of pharmaceutical interest. Compared with single-pharmacophore DELs, dual-pharmacophore DELs simultaneously display two chemical moieties on both DNA strands, and allow for the construction of highly diverse and pure libraries, with a potential for targeting larger protein surfaces. Although methods for the encoding of simple, fragment-like dual-display libraries have been established, more complex libraries require a different encoding strategy. Here, we present a robust and convenient “large encoding design” (LED), which facilitates the PCR-amplification of multiple codes distributed among two partially complementary DNA strands. We experimentally implemented multiple coding regions and we compared the new DNA encoding scheme with previously reported dual-display DEL modalities in terms of amplifiability and performance in test selections against two target proteins. With the LED methodology in place, we foresee the construction and screening of DELs of unprecedented sizes and designs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...