High-strength, high-toughness, self-healing thermosetting shape memory polyurethane enabled by dual dynamic covalent bonds†
Abstract
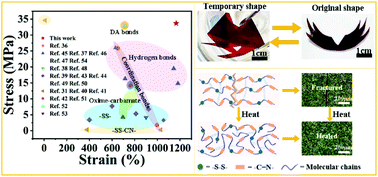
Smart materials that integrate multiple functions into one system broaden the application range of materials, but there are still challenges to obtaining a material with excellent shape memory, toughness, and self-healing. Herein, we prepared a high-strength and high-toughness thermosetting shape memory polyurethane with the aid of a chain extender containing dual dynamic covalent bonds, which showed excellent self-healing effects. Compared with PUs that contain only disulfide bonds or imine bonds, elastomers with dual dynamic covalent bonds possess superior mechanical properties. The maximum tensile strength and breaking elongation of elastomer PU-SS-CN-12.5% are 33.70 ± 4.25 MPa and 1137.72 ± 81.29%, respectively, and it also presents a high toughness of 197.35 ± 35.33 MJ m−3. Surprisingly, PU-SS-CN-12.5% demonstrates excellent low-temperature flexibility, and can deform arbitrarily at −50 °C. In addition, all PUs exhibit shape memory properties, which can be fixed at −60 °C. The shape fixation rate is approximately 90%, and they can recover immediately at 60 °C; the shape recovery rate is approximately 95%. The elastomers also have the capacity of self-healing resulting from the existence of dynamic covalent bonds. The healing efficiency of PU-SS-CN-15% is close to 100%, and it can also be recycled by hot-pressing at 120 °C and 3 MPa for 24 h. Due to its excellent properties, it might have significant potential as a low-temperature smart material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...