How different are marine microbial natural products compared to their terrestrial counterparts?†
Abstract
Covering: 1877 to 2020
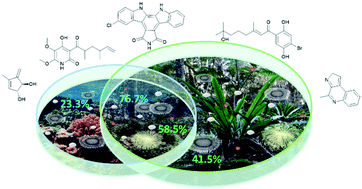
A key challenge in natural products research is the selection of biodiversity to yield novel chemistry. Recently, marine microorganisms have become a preferred source. But how novel are marine microorganism natural products compared to those reported from terrestrial microbes? Cluster analysis of chemical fingerprints and molecular scaffold analysis of 55 817 compounds reported from marine and terrestrial microorganisms, and marine macro-organisms showed that 76.7% of the compounds isolated from marine microorganisms are closely related to compounds isolated from terrestrial microorganisms. Only 14.3% of marine microorganism natural products are unique when marine macro-organism natural products are also considered. Studies targeting marine specific and understudied microbial phyla result in a higher likelihood of finding marine specific compounds, whereas the depth and geographic location of microorganism collection have little influence. We recommend marine targeted strain isolation, incorporating early use of genomic sequencing to guide strain selection, innovation in culture media and cultivation techniques and the application of cheminformatics tools to focus on unique natural product diversity, rather than the dereplication of known compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...