Marine paralytic shellfish toxins: chemical properties, mode of action, newer analogues, and structure–toxicity relationship†
Abstract
Up to the end of 2020
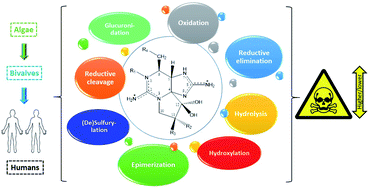
Every year, the appearance of marine biotoxins causes enormous socio-economic damage worldwide. Among the major groups of biotoxins, paralytic shellfish toxins, comprising saxitoxin and its analogues (STXs), are the ones that cause the most severe effects on humans, including death. However, the knowledge that currently exists on their chemistry, properties and mode of toxicological action is disperse and partially outdated. This review intends to systematically compile the dispersed information, updating and complementing it. With this purpose, it addresses several aspects related to the molecular structure of these toxins. Special focus is given to the bioconversion reactions that may occur in the different organisms (dinoflagellates, bivalves, and humans) and the possible mediators involved. A critical review of the most recently discovered analogues, the M-series toxins, is presented. Finally, a deep discussion about the relationship between the molecular structure (e.g., effect of the substituting groups and the net charge of the molecules) and the toxic activity of these molecules is performed, proposing the concept of “toxicological traffic light” based on the toxicity equivalency factors (TEFs).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...